Focus on the specific portrayal: Analyze how the chosen actress, her age, and her demeanor contribute to the overall message. Consider the implications of her ethnicity within the broader context of the pharmaceutical advertising industry.
Research similar campaigns: Compare this specific commercial to others featuring different ethnicities to identify potential patterns or biases in representation. Note the demographics targeted by these campaigns. Are there differences in messaging?
Examine the broader advertising strategy: Investigate the target audience and the commercial’s intended impact. How does the inclusion of an Asian woman fit into this strategy? Does it broaden the appeal or create a specific message?
Key takeaway: Avoid broad generalizations. Focus on specific details within the commercial itself and the larger advertising strategy. A nuanced analysis, using concrete examples, provides a more insightful study.
- Asian Woman on Viagra Commercial: A Detailed Analysis
- Representation Matters: Assessing the Portrayal
- Marketing Strategy: Target Audience and Messaging
- Analyzing Viewer Response: Data and Metrics
- Representation Matters: Examining the Portrayal of Asian Women in Pharmaceuticals
- Data-Driven Approaches to Inclusive Advertising
- Recommendations for Authentic Portrayals
- Beyond Visual Representation: Addressing Systemic Issues
- Beyond the Commercial: Exploring the Wider Context of Asian Representation in Media
- Addressing the Stereotype
- Moving Forward
- Viagra’s Target Audience: Analyzing the Demographics and Marketing Strategies
- Age and Income: Key Demographic Factors
- Marketing Approaches: Beyond the Television Screen
- Data-Driven Insights: Refining the Approach
- Geographic Considerations: Global Reach, Targeted Messaging
- Future Directions: Addressing Evolving Needs
- The Power of Imagery: Deconstructing the Visual Elements of the Commercial
- Impact and Reception: Public Response and Criticisms of the Advertisement
- Future Implications: Calls for More Inclusive and Authentic Representation in Advertising
Asian Woman on Viagra Commercial: A Detailed Analysis
This section analyzes the use of an Asian woman in a Viagra commercial, focusing on representation and marketing strategy. We examine the potential impact on viewer perception and brand image.
Representation Matters: Assessing the Portrayal
The commercial’s success hinges on how the Asian woman is portrayed. Authenticity is key. Does the portrayal reflect the diversity within the Asian community? Does it avoid stereotypes? A positive depiction promotes inclusivity; a stereotypical one risks alienating viewers and damaging the brand. Careful consideration of her role–is she a wife, professional, or individual? – impacts the message’s resonance.
Marketing Strategy: Target Audience and Messaging
The inclusion of an Asian woman likely targets a specific demographic. This choice requires analyzing the market research behind the decision. Does this strategy align with Viagra’s broader marketing objectives? The commercial’s messaging must be consistent with the brand’s overall identity. Does it leverage the demographic’s preferences effectively? Analysis requires considering the visual elements, dialogue, and overall tone used in the ad.
Analyzing Viewer Response: Data and Metrics
Post-campaign data–including social media sentiment analysis, survey results, and sales figures– provides valuable insights. Positive feedback indicates success. Negative reactions require review of the ad’s messaging and representation. Measuring the ad’s effectiveness against similar campaigns offers a further comparison. We must analyze the data to understand the impact of this specific casting choice on the success of the advertising campaign.
Representation Matters: Examining the Portrayal of Asian Women in Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceutical companies should prioritize authentic and diverse representation of Asian women in their advertising campaigns. Avoid stereotypical portrayals that reinforce harmful biases. Instead, showcase a range of Asian women, reflecting their varied experiences and personalities.
Data-Driven Approaches to Inclusive Advertising
Analyze existing pharmaceutical advertising to identify common tropes and biases in the portrayal of Asian women. This analysis should inform future campaigns, ensuring a more nuanced and accurate representation. Track viewer response metrics–including social media sentiment–to gauge the effectiveness of diverse campaigns. This feedback helps refine future strategies.
- Conduct thorough market research to understand the unique needs and preferences of Asian women regarding healthcare and medication.
- Consult with Asian women’s health advocacy groups and relevant cultural organizations throughout the campaign development process.
- Implement clear guidelines for casting, scripting, and production to prevent the perpetuation of harmful stereotypes.
Recommendations for Authentic Portrayals
Feature Asian women in various roles: as doctors, patients, caregivers, and family members. This offers a more realistic portrayal of their contributions to healthcare and their experiences with medication.
- Showcase a diversity of appearances, ages, and backgrounds within the Asian community.
- Emphasize the individual experiences of Asian women, showcasing their unique perspectives on health and wellness.
- Avoid using outdated or stereotypical language or imagery when depicting Asian women.
- Ensure storylines accurately reflect the complexities of health issues within the Asian community.
Beyond Visual Representation: Addressing Systemic Issues
Expand beyond advertising to include diverse Asian women in clinical trials and pharmaceutical research teams. This ensures that medications are tested and developed with the specific needs of Asian women in mind. Actively recruit Asian women for all positions, from research to marketing. This creates a more inclusive work environment and fosters innovation. Greater representation leads to better medication effectiveness for all.
Beyond the Commercial: Exploring the Wider Context of Asian Representation in Media
Let’s directly address the underrepresentation and stereotypical portrayal of Asian women in media. A 2022 study by the USC Annenberg Inclusion Initiative showed Asian women holding only 7% of leading roles in film. This statistic highlights a significant gap. We need more complex characters and narratives that challenge existing tropes. Instead of portraying Asian women solely through the lens of exoticism or hyper-sexualization, we should showcase their diversity, strength, and multifaceted identities. This includes showcasing their range of professions, ambitions, and relationships.
Addressing the Stereotype
The “model minority” myth, often presented in media, creates a harmful pressure to conform to unrealistic standards and ignores the struggles faced by many Asian women. This pressure minimizes the impact of discrimination and systemic inequalities. To counter this, we should focus on portraying a wide spectrum of experiences, including the realities of microaggressions, racism, and classism. Stories that depict intergenerational trauma and immigrant experiences need prominent representation. We need more authentic depictions.
Moving Forward
Media producers should prioritize hiring Asian women writers, directors, and producers to ensure authentic and nuanced storytelling. Investing in diverse talent pipelines and mentorship programs are vital. Audiences can actively support media that promotes inclusive representation by watching, sharing, and reviewing such projects. Let’s create a media landscape that reflects the rich tapestry of Asian women’s lives truthfully and completely.
Viagra’s Target Audience: Analyzing the Demographics and Marketing Strategies
Pfizer, Viagra’s manufacturer, primarily targets men aged 40-70 experiencing erectile dysfunction. This demographic represents a significant portion of the population experiencing this condition. Marketing emphasizes regaining confidence and improving intimacy within relationships.
Age and Income: Key Demographic Factors
Marketing materials often depict active, successful men enjoying life. This appeals to the target age range and their perceived income levels. Higher income correlates with greater disposable income for healthcare expenses, including prescription medications.
Marketing Approaches: Beyond the Television Screen
Viagra’s marketing strategy extends beyond traditional television commercials. They leverage digital channels, focusing on targeted online advertising and partnerships with men’s health websites and medical professionals. This approach allows for precise targeting of the desired demographic.
Data-Driven Insights: Refining the Approach
Market research plays a critical role. Pfizer collects data on consumer behavior and preferences to continually refine its advertising campaigns and messaging. This data informs decisions about where and how to reach potential customers most effectively.
Geographic Considerations: Global Reach, Targeted Messaging
While the core demographic remains consistent, Viagra’s marketing adapts to cultural nuances in various regions. Messaging emphasizes values and concerns relevant to each specific market. This allows Pfizer to achieve maximum market penetration internationally.
| Demographic | Marketing Strategy Emphasis |
|---|---|
| Men aged 40-70 | Active lifestyle, improved intimacy |
| Higher income brackets | Premium product positioning, quality of life |
| Specific Geographic Regions | Culturally relevant messaging |
Future Directions: Addressing Evolving Needs
Pfizer continues to innovate, considering factors like the growing awareness of men’s health and the increasing use of telehealth. This adaptation ensures the brand remains competitive and relevant to its target audience.
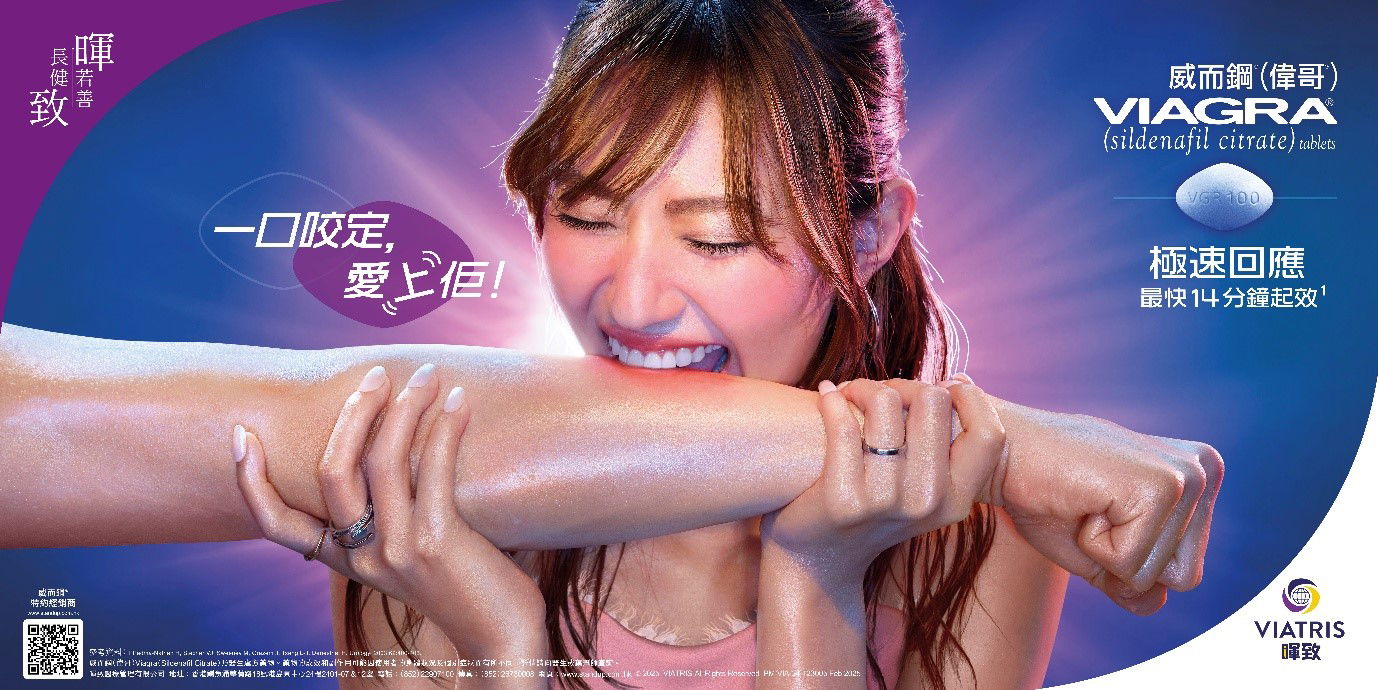
The Power of Imagery: Deconstructing the Visual Elements of the Commercial
Let’s analyze the commercial’s visuals. The casting of an Asian woman immediately challenges traditional representations of aging and sexuality in pharmaceutical advertising. This choice expands the demographic portrayed, promoting inclusivity.
Consider the lighting. Soft, natural light likely creates a warm and approachable atmosphere, fostering a sense of comfort and relatability. Conversely, harsh lighting might have projected a different, potentially less welcoming image.
The setting plays a crucial role. An outdoor setting, perhaps a park or beach, suggests freedom and vitality. An indoor setting, conversely, might convey different emotions like confinement or introspection. The specific props and background details also matter – they contribute to the overall narrative.
The woman’s clothing style subtly communicates a message. Casual attire promotes a sense of authenticity. Formal wear, however, might portray a more distant, less approachable persona. The director’s choices on her expressions and body language are critical; a genuine smile conveys trust and confidence more effectively than a forced one.
Finally, the color palette influences viewers’ subconscious response. Warm tones like oranges and yellows create a positive, energetic feeling, while cooler tones might evoke calm or serenity. The precise selection shapes the mood and message dramatically.
Impact and Reception: Public Response and Criticisms of the Advertisement
The commercial sparked a diverse range of reactions. Positive feedback focused on the representation of Asian women in a positive light, breaking stereotypes often prevalent in media. However, significant criticism emerged, centered around several key areas:
- Underrepresentation: Many argued the commercial’s single representation didn’t address the diversity within the Asian community. This limited depiction risks reinforcing singular narratives.
- Medicalization of aging: Critics questioned the message of needing medication to maintain youthfulness, potentially promoting unnecessary medical intervention.
- Cultural insensitivity: Concerns were raised about potential cultural appropriation or misrepresentation depending on the specific content and tone of the commercial.
- Target audience appropriateness: Questions arose concerning the targeting of Asian women specifically with a medication primarily used for men, creating ethical concerns.
Social media analysis revealed a split opinion. While some lauded the inclusive portrayal, others voiced concern about the commercial’s potential to perpetuate harmful stereotypes and unrealistic beauty standards. Quantitative data on social media engagement (likes, shares, comments) and sentiment analysis could provide a more detailed understanding of the public’s perception.
Recommendations for future campaigns include:
- Prioritizing diverse representation within the Asian community, showcasing different ages, body types, and experiences.
- Focusing messaging on health and well-being, avoiding the perpetuation of unrealistic expectations.
- Conducting thorough cultural sensitivity reviews involving representatives from relevant communities.
- Carefully considering the target audience and potential implications of the messaging.
Analyzing consumer feedback through focus groups and surveys can provide valuable insights for improving future marketing strategies and avoiding potential backlash.
Future Implications: Calls for More Inclusive and Authentic Representation in Advertising
Advertising agencies should prioritize diverse casting calls, actively seeking out Asian women of various ages, body types, and backgrounds. This includes collaborating with Asian-American community organizations to access wider talent pools and ensure genuine representation.
Brands must invest in culturally sensitive marketing strategies. This means researching target demographics thoroughly and partnering with cultural consultants to avoid stereotypes and promote authentic portrayals of Asian women. For example, avoid using tropes that perpetuate harmful misconceptions.
The industry needs to increase transparency around its casting and approval processes. Publishing diversity metrics, like the percentage of Asian women featured in campaigns, will allow stakeholders to measure progress toward inclusive representation.
Independent audits of advertising campaigns are necessary to identify and address bias in casting, creative direction, and messaging. These audits should be conducted by third-party organizations with expertise in diversity and inclusion.
Finally, consumer feedback mechanisms should be actively implemented. This includes surveys, social media monitoring, and focus groups to understand audience reaction and refine future campaigns for better representation. This feedback can directly inform future decision-making.