Seeking information on the average age of Viagra users? The average age is generally between 50 and 60, though many men in their 40s and beyond 70 also use it. This isn’t a strict boundary; individual needs and doctor’s recommendations vary greatly.
Factors influencing Viagra use include erectile dysfunction severity, overall health, and response to treatment. Your doctor will consider your specific medical history and lifestyle before recommending Viagra or exploring alternative options. Open communication with your physician is paramount.
Remember, Viagra isn’t suitable for everyone. Pre-existing conditions like heart disease or high blood pressure require careful evaluation before prescribing. Always discuss potential side effects and drug interactions with your healthcare provider. They can help you make an informed decision and ensure your safety.
Finding the right treatment plan requires a professional consultation. Don’t self-medicate; always seek guidance from a qualified doctor. They possess the expertise to assess your individual circumstances and suggest the best course of action for your specific needs.
- Average Age for Viagra: A Detailed Look
- Factors Influencing Viagra Use Age
- Age and Viagra Prescription: What to Expect
- Viagra and Older Men
- Younger Men and Viagra
- Viagra’s Intended Use and Age Range
- Average Age of Viagra Users: Data and Statistics
- Factors Influencing Viagra Prescription Age
- Health Risks and Considerations Associated with Age and Viagra
- Hearing and Vision Changes
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Interactions with Medications
- Pre-existing Conditions
- Alternatives to Viagra for Older Men
- Medication Alternatives
- Non-Medication Options
- Choosing the Right Approach
- Seeking Professional Guidance
- When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Viagra Use
- Specific Health Concerns Requiring Medical Attention
Average Age for Viagra: A Detailed Look
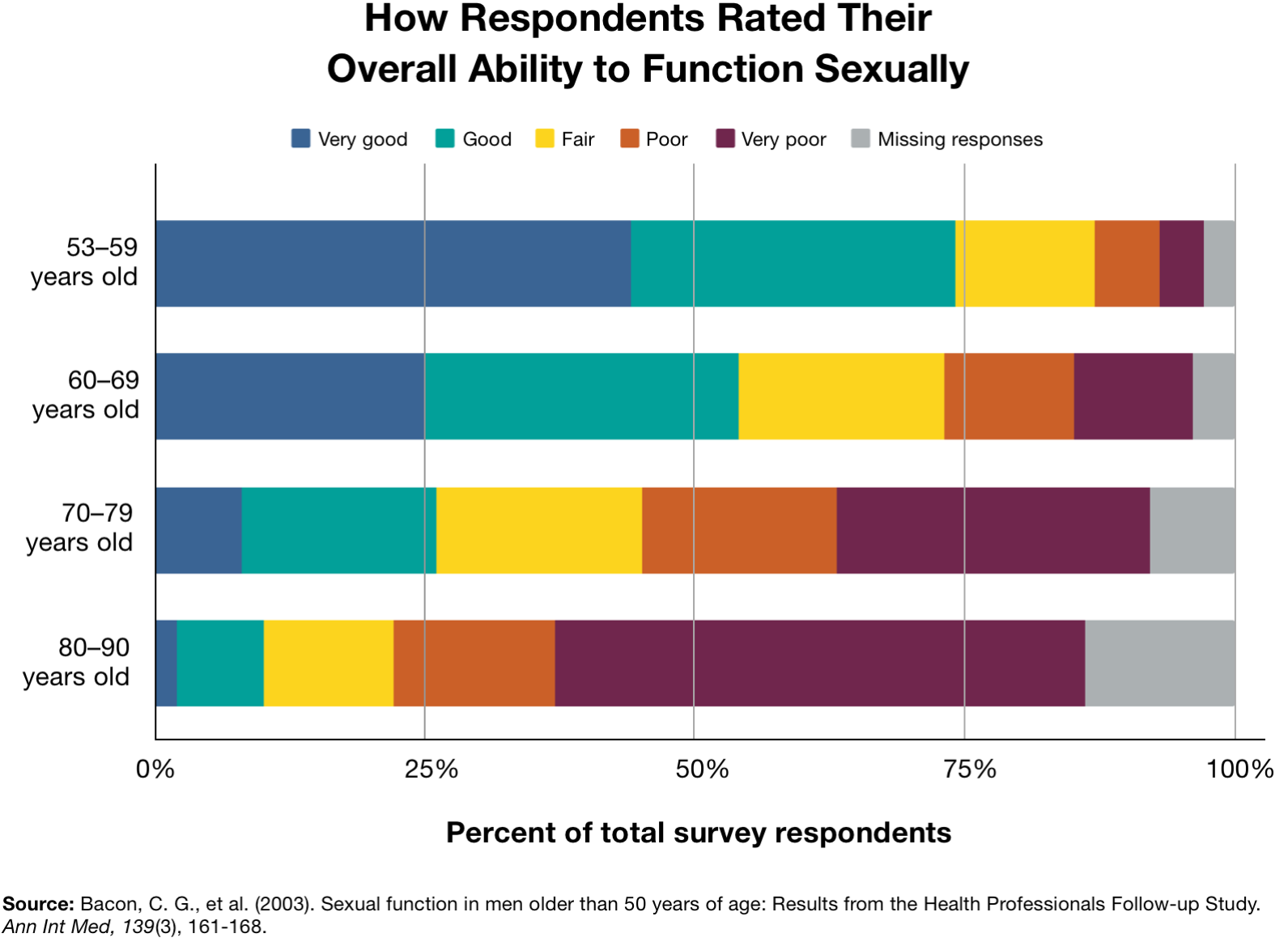
The average age of men using Viagra is around 65. However, this is just an average; the actual age range is quite broad.
Factors Influencing Viagra Use Age
- Underlying health conditions: Viagra is prescribed to treat erectile dysfunction, often linked to age-related health issues like heart disease and diabetes. These conditions can manifest at different ages.
- Lifestyle choices: Smoking, poor diet, and lack of exercise contribute to erectile dysfunction, potentially impacting the age at which men seek treatment.
- Individual variation: Erectile dysfunction onset and severity vary greatly from person to person. Some men experience it earlier than others.
It’s important to remember that age is only one factor. A doctor assesses individual health before prescribing Viagra.
Age and Viagra Prescription: What to Expect
- Thorough medical evaluation: Before prescribing Viagra, your doctor will perform a comprehensive medical history review and physical examination. This helps determine suitability and potential risks.
- Discussion of alternatives: If Viagra is deemed unsuitable, or if side effects occur, other treatments for erectile dysfunction will be discussed.
- Monitoring for side effects: Regular check-ups allow for monitoring of potential side effects and adjustments to dosage, if needed. Open communication with your doctor is crucial.
Viagra and Older Men
While many older men benefit from Viagra, doctors carefully consider age-related health concerns when prescribing. They might adjust dosages or recommend alternative treatments based on individual circumstances.
Younger Men and Viagra
While less common, younger men can also experience erectile dysfunction. Underlying medical issues or psychological factors are often involved. A doctor can help determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Viagra’s Intended Use and Age Range
Viagra, or sildenafil citrate, treats erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. The FDA approved it for men 18 and older.
While Viagra is approved for use in this age group, doctors consider individual factors like overall health and potential drug interactions. A comprehensive medical history is crucial before prescribing Viagra.
Older men frequently experience ED, and Viagra can be a suitable treatment option, but age itself isn’t a barrier to treatment. A thorough assessment by a physician is always necessary to determine suitability and safe dosage.
Men with pre-existing conditions like heart disease or high blood pressure may need adjusted dosages or alternative treatments. Open communication with your doctor about your medical history is vital.
Consult your doctor to discuss if Viagra is the right treatment for you, considering your individual health profile and age. They will help determine the appropriate course of action.
Average Age of Viagra Users: Data and Statistics
The average age of Viagra users is around 65, though this varies significantly depending on the study and the specific population sampled. Studies show a broad range, with a notable portion of users falling between 55 and 75 years old.
Several factors influence this average. Increased prevalence of erectile dysfunction (ED) with age contributes to higher numbers in older age brackets. However, younger men (40-55) also utilize Viagra, primarily to address ED stemming from underlying health conditions or lifestyle choices.
Data from pharmaceutical companies suggest a gradual increase in Viagra prescriptions for men under 50 in recent years, potentially reflecting changing attitudes towards ED treatment and improved access to healthcare. However, the majority of prescriptions still target the 55-75 age range.
It’s important to note that these statistics represent averages. Individual experiences vary considerably. Age is just one factor among many affecting ED and treatment choices.
Further research focusing on specific demographics and health conditions is needed for a clearer picture of Viagra usage patterns across different age groups. Consulting a physician for personalized advice is always recommended.
Factors Influencing Viagra Prescription Age
Doctors primarily consider a patient’s medical history when determining Viagra prescription appropriateness. This includes assessing cardiovascular health, as Viagra can affect blood pressure. Men with heart conditions, high blood pressure, or a history of stroke require careful evaluation before receiving a prescription.
The presence of other health issues also plays a significant role. Conditions like liver or kidney disease can impact how the body processes Viagra, potentially leading to adverse effects. Therefore, a thorough review of a patient’s complete medical profile is crucial.
Lifestyle factors matter. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of side effects. Doctors account for these habits during the prescription process, potentially adjusting dosage or recommending lifestyle changes.
Concurrent medications are another vital consideration. Some medications interact negatively with Viagra, potentially leading to dangerous interactions. A complete list of all current medications is necessary for a safe prescription.
Finally, the patient’s individual response to Viagra is paramount. Some men experience side effects at lower doses. This necessitates careful monitoring and potential dosage adjustments, guided by the patient’s response.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication, including Viagra.
Health Risks and Considerations Associated with Age and Viagra
Men over 50 taking Viagra should discuss potential cardiovascular risks with their doctor. Viagra, or sildenafil, can lower blood pressure, potentially causing dizziness or fainting, especially when combined with nitrates or alpha-blockers commonly prescribed for heart conditions. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is recommended.
Hearing and Vision Changes
While rare, some men report temporary vision disturbances, like blurred vision or blue-tinged vision, after taking Viagra. Similarly, temporary hearing loss or tinnitus has been reported. These effects are usually mild and transient, but immediate medical attention is needed if they persist or worsen. Your doctor can assess your risk factors and provide guidance.
Other Potential Side Effects
Older men are more likely to experience side effects like headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, and indigestion. These are often mild but can impact quality of life. Inform your physician about any pre-existing conditions, such as kidney or liver disease, as these can affect how your body processes Viagra. Your doctor will help you determine the appropriate dosage and frequency of use.
Interactions with Medications
Many medications interact with Viagra. This includes heart medications, blood pressure medications, and antidepressants. Always provide your doctor with a complete list of your current medications and supplements before starting Viagra. Failure to disclose medication information can lead to serious adverse health events.
Pre-existing Conditions
Men with heart disease, high blood pressure, or stroke history face increased risks when using Viagra. Open communication with your cardiologist is crucial before initiating treatment. A thorough physical examination and possibly some tests are needed to assess your suitability for Viagra. Your doctor may recommend alternative treatment options.
Alternatives to Viagra for Older Men
Consider lifestyle changes first. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management significantly improve blood flow, a key factor in erectile function. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Focus on fruits, vegetables, and lean protein. Losing even a small amount of weight can make a noticeable difference.
Medication Alternatives
Your doctor might suggest alternative medications. These include phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors like tadalafil (Cialis) or avanafil (Stendra), each with slightly different properties and side effect profiles. They work similarly to Viagra but may offer longer-lasting effects or be better suited to specific health conditions. Another option is alprostadil, available as a urethral suppository or injection. Discuss the potential benefits and risks of each with your physician.
Non-Medication Options
Vacuum erection devices (VEDs) are non-invasive and can be used at home. A VED creates a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood into it. While effective for many, some men find them cumbersome. Penile implants are a surgical option providing permanent erectile rigidity. This is generally considered for men who haven’t had success with other treatments.
Choosing the Right Approach
The best approach depends on individual health, preferences, and the cause of erectile dysfunction. Talking to your doctor is crucial for a personalized plan. They can assess your overall health, identify potential underlying issues, and recommend the most appropriate treatment.
| Alternative | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lifestyle Changes | Diet, exercise, weight loss | Non-invasive, long-term benefits | Requires commitment, may not be sufficient alone |
| PDE5 Inhibitors (Cialis, Stendra) | Oral medications | Relatively easy to use, effective for many | Potential side effects, not suitable for everyone |
| Alprostadil | Urethral suppository or injection | Effective when other treatments fail | Can cause discomfort or side effects |
| Vacuum Erection Device (VED) | External device | Non-invasive, relatively simple | Can be cumbersome, may not be effective for all |
| Penile Implants | Surgical procedure | Permanent solution | Surgical risks, irreversible |
Seeking Professional Guidance
Remember, open communication with your doctor is key. They can accurately diagnose the root cause of erectile dysfunction and develop a tailored treatment plan that addresses your specific needs. Don’t hesitate to discuss your concerns and ask questions.
When to Consult a Doctor Regarding Viagra Use
Schedule a doctor’s appointment before starting Viagra if you have heart problems, high or low blood pressure, a history of strokes, or any kidney or liver disease. Discuss any medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, as interactions can occur. This is particularly important with nitrates, which can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure when combined with Viagra.
Specific Health Concerns Requiring Medical Attention
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience chest pain, dizziness, or prolonged erection (priapism) lasting more than four hours after taking Viagra. These are serious side effects requiring prompt medical intervention. Also consult your doctor if you experience sudden vision loss or hearing problems. Regular monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels is advised, especially if you have pre-existing conditions. Discuss any changes in your sexual health, including decreased libido or performance issues, with your physician for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. They can help determine if Viagra is the right choice for you, and assess for underlying medical issues.