Consider seeking a consultation with a healthcare professional before making any decisions about Viagra or similar medications. They can provide personalized advice based on your medical history and individual needs, ensuring safe and effective treatment.
Viagra, or sildenafil, primarily treats erectile dysfunction by increasing blood flow to the penis. However, numerous other medications exist, each with its unique mechanism of action and potential side effects. Your doctor can explain these differences and help you choose the best option.
Lifestyle changes often significantly impact erectile function. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management techniques, and limiting alcohol and tobacco consumption can dramatically improve results. Coupling these changes with medication, if necessary, provides a holistic approach to treatment.
Always discuss potential drug interactions with your doctor. Certain medications can negatively interact with Viagra or alternative treatments. A thorough review of your current medications is critical for safe use.
Remember: Open communication with your healthcare provider is key. Don’t hesitate to ask questions about side effects, efficacy, and alternative treatments. They are there to support you in finding the right solution.
- What is Viagra?
- How Viagra Works
- PDE5 Inhibition and Blood Flow
- The Erection Process
- Factors Affecting Viagra’s Efficacy
- Important Considerations
- Dosage and Administration
- Viagra Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects and Risks
- Alternatives to Viagra
- Non-Medication Approaches
- Comparison Table
- Counseling and Therapy
What is Viagra?
Viagra, or sildenafil citrate, is a medication primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). It works by increasing blood flow to the penis, enabling a firmer erection.
Your doctor will determine the appropriate dosage, typically starting with a 50mg tablet. Always follow their instructions precisely. Common side effects include headache, flushing, and nasal congestion, usually mild and temporary.
Viagra isn’t suitable for everyone. Men with heart conditions, low blood pressure, or certain eye problems should discuss its use with their physician before taking it. It also interacts with some medications, so provide your doctor with a complete list of your current prescriptions and over-the-counter drugs.
Important Note: This information doesn’t substitute professional medical advice. Consult your doctor to discuss if Viagra is right for you and to address any concerns.
Remember: Self-medicating can be dangerous. Always seek professional medical guidance.
How Viagra Works
Viagra, or sildenafil, primarily enhances erections by increasing blood flow to the penis. This happens because it inhibits an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5).
PDE5 Inhibition and Blood Flow
PDE5 normally breaks down a molecule called cyclic GMP (cGMP). cGMP relaxes the muscles in the penis, allowing blood vessels to widen and fill with blood. By blocking PDE5, Viagra allows cGMP levels to rise, leading to increased blood flow and a stronger erection.
The Erection Process
- Sexual stimulation triggers the release of nitric oxide.
- Nitric oxide activates an enzyme that increases cGMP levels.
- Increased cGMP relaxes smooth muscles in the penis.
- Blood vessels widen, increasing blood flow.
- This increased blood flow causes an erection.
- Viagra prolongs the effects of cGMP by inhibiting PDE5.
Factors Affecting Viagra’s Efficacy
- Underlying health conditions, such as heart disease or diabetes, can impact blood flow and Viagra’s effectiveness.
- Certain medications can interact with Viagra, potentially reducing its efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking.
- Individual responses to Viagra vary. Some men experience a stronger effect than others.
Important Considerations
Viagra is a prescription medication and should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. They can assess your overall health and determine if Viagra is a safe and appropriate treatment option for you.
Dosage and Administration
Your doctor will prescribe the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and health status. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully regarding dosage and timing. Typically, Viagra is taken approximately 30-60 minutes before sexual activity.
Viagra Dosage and Administration
Begin with your doctor’s prescribed dose. This is crucial for your safety and effectiveness.
The typical starting dose is 50mg, taken as needed, about an hour before sexual activity. Your doctor might adjust this depending on your response and individual health.
Never exceed 100mg in a 24-hour period. Higher doses don’t necessarily improve results and increase the risk of side effects.
Take Viagra with a glass of water. Food may delay absorption, so consider timing your dose accordingly.
Certain medications can interact negatively with Viagra. Always inform your doctor of all medications and supplements you’re taking.
Avoid alcohol in excessive amounts when using Viagra, as it can worsen side effects.
If you experience side effects like vision changes or chest pain, seek immediate medical attention.
Remember, Viagra is only effective for erectile dysfunction. If you have other health concerns, discuss them with your physician.
Regular check-ups with your doctor are recommended to monitor your progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
Viagra, like all medications, carries potential side effects. Common side effects include headache, facial flushing, nasal congestion, and upset stomach. These are usually mild and temporary.
More serious, though less common, side effects include vision changes (blurred vision, blue-tinged vision), hearing loss, and prolonged erection (priapism). Seek immediate medical attention if you experience a prolonged erection lasting more than four hours. This condition requires urgent treatment to prevent permanent damage.
Heart problems are another potential risk. Viagra can lower blood pressure, so it’s crucial to inform your doctor about any pre-existing heart conditions before using it. People with severe heart disease, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or recently suffered a heart attack or stroke should avoid Viagra.
Interactions with other medications are possible. Viagra can interact with nitrates used to treat angina, leading to a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Always discuss all medications you are taking with your doctor before starting Viagra.
Rare but serious side effects include sudden hearing loss and vision problems. If you experience any sudden changes in your hearing or vision, discontinue use and contact a medical professional immediately.
Remember to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and report any concerning side effects. Open communication with your physician ensures safe and effective use of Viagra.
Alternatives to Viagra
Consider Cialis (tadalafil) for longer-lasting effects, potentially up to 36 hours. It’s a different medication with a similar mechanism, offering flexibility in timing.
Another option is Levitra (vardenafil), which acts similarly to Viagra but may have a slightly faster onset. Consult your doctor to determine which is best suited for you.
Lifestyle changes often significantly improve erectile function. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management all contribute positively. Reducing alcohol and tobacco consumption is equally crucial.
Non-Medication Approaches
Penile implants offer a surgical solution for severe erectile dysfunction. This involves placing an implant inside the penis to facilitate erection. Discuss this option with your urologist to understand potential benefits and risks.
Vacuum erection devices create a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood in and causing an erection. These are non-invasive and can be used at home. However, they are not suitable for everyone.
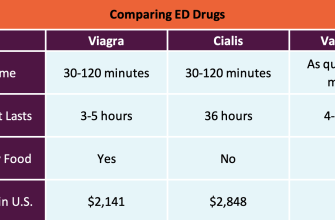
Comparison Table
| Medication | Duration of Effect | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Viagra (sildenafil) | 4-5 hours | Headache, flushing, nasal congestion |
| Cialis (tadalafil) | Up to 36 hours | Back pain, muscle aches |
| Levitra (vardenafil) | 4-5 hours | Headache, flushing, indigestion |
Counseling and Therapy
Psychological factors can contribute to erectile dysfunction. Therapy, particularly sex therapy, can help address underlying anxieties and improve performance. This approach may be beneficial in conjunction with medical treatments.