The recommended starting dose of Viagra is 50mg, taken as needed, about one hour before sexual activity. This dose suits many men, providing effective results with manageable side effects.
Your doctor may adjust this, depending on your individual response and health conditions. A lower dose of 25mg might be prescribed if you experience side effects like headaches or flushing. Conversely, if 50mg proves insufficient, your physician could increase it to 100mg, but this is generally the maximum recommended dose.
Important Note: Never exceed the prescribed dosage. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully. They’ll consider your overall health and any other medications you’re taking to determine the safest and most effective dosage for you.
Remember to discuss any concerns or questions regarding Viagra with your healthcare provider before starting treatment. They can provide personalized guidance and address any potential risks or interactions with other medications.
- Recommended Viagra Dose
- Understanding the Standard Viagra Dosage
- Adjusting Your Dose
- Important Considerations
- Frequency of Use
- Side Effects
- Seeking Medical Advice
- Adjusting Viagra Dosage Based on Response
- Viagra Dosage and Interactions with Other Medications
- Medications Affecting Viagra’s Effectiveness
- Potential Side Effects and Interactions
- Specific Medication Interactions
Recommended Viagra Dose
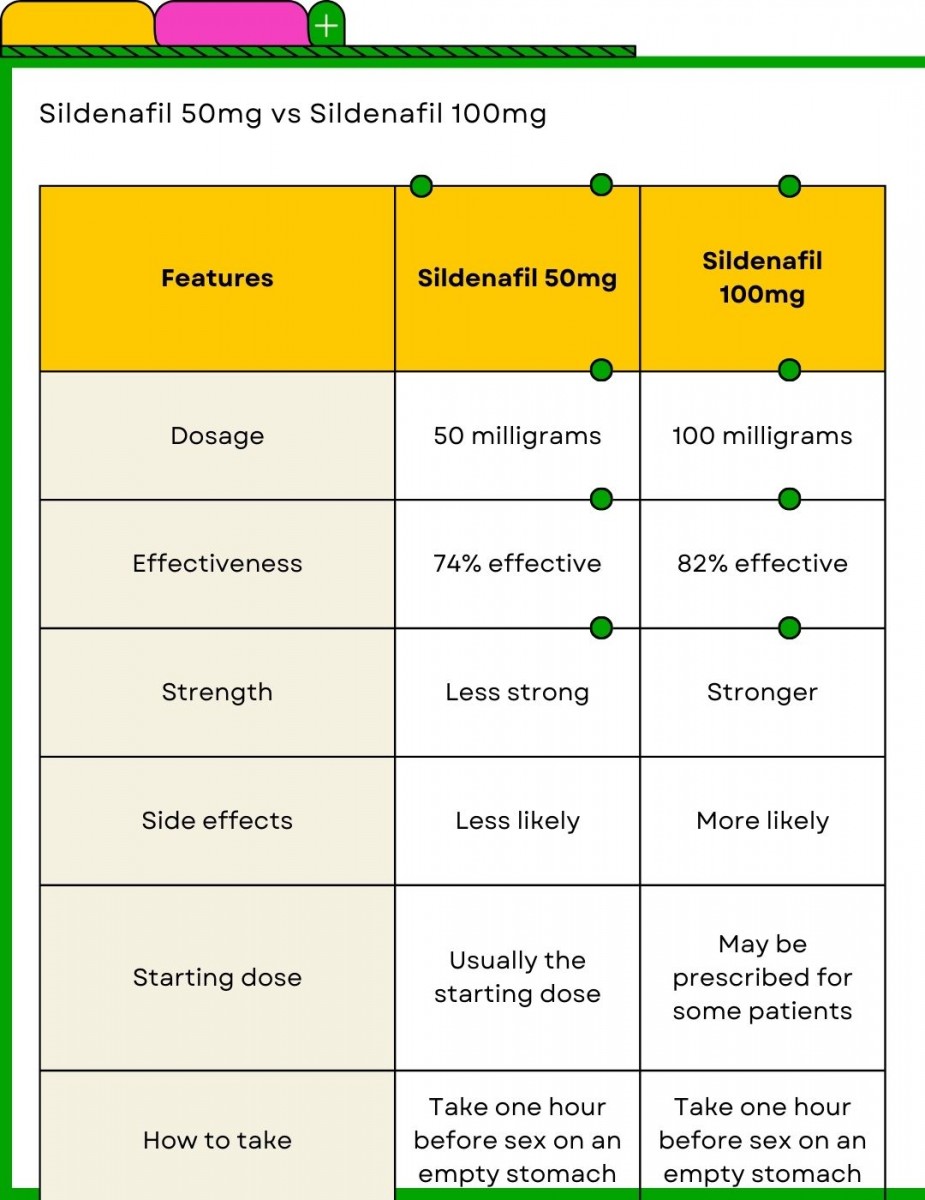
The typical starting dose of Viagra is 50 mg, taken as needed, about one hour before sexual activity. This dose works well for many men.
Your doctor may recommend a lower dose of 25 mg if you’re older, have certain health conditions, or are taking other medications that interact with Viagra.
Conversely, if 50 mg isn’t effective enough, your doctor might increase your dose to 100 mg. However, this is the maximum recommended dose.
Remember, never exceed the recommended dose without your doctor’s explicit approval. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
The frequency of use depends on individual needs and your doctor’s guidance. It’s typically not recommended to take Viagra more than once per day.
Factors like your age, overall health, and other medications you are taking heavily influence the appropriate Viagra dosage. Open communication with your physician is paramount.
If you experience side effects, contact your doctor immediately. Common side effects can include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances.
Understanding the Standard Viagra Dosage
The standard starting dose for Viagra is 50mg. This dose is suitable for most men.
Adjusting Your Dose
Your doctor may adjust this based on your response and any pre-existing health conditions. They might recommend a lower dose (25mg) if you experience side effects or a higher dose (100mg) if 50mg isn’t effective. However, 100mg is the maximum recommended dose.
- Never exceed the prescribed dose.
- Take Viagra only as directed by your physician.
Important Considerations
Several factors influence the appropriate Viagra dosage. These include:
- Your age
- Your overall health
- Other medications you are taking
- The severity of your erectile dysfunction
Frequency of Use
Viagra is typically taken as needed, approximately 30-60 minutes before sexual activity. It’s not intended for daily use, and your doctor will advise on appropriate frequency.
Side Effects
Common side effects include headache, flushing, and nasal congestion. Serious side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention. Consult your doctor if you experience any concerning symptoms.
Seeking Medical Advice
This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication, including Viagra, to determine the right dosage and address any potential health concerns.
Adjusting Viagra Dosage Based on Response
Start with the recommended dose of 50mg. Take it about an hour before sexual activity.
If 50mg is effective: Maintain this dose. There’s no need to increase it unless you experience a decrease in effectiveness over time.
If 50mg is not effective: Your doctor may increase the dose to 100mg. This is the maximum recommended dose.
Important Note: Never exceed 100mg without consulting your physician. Higher doses don’t necessarily mean better results and can increase the risk of side effects.
If 100mg is too strong: Your doctor can lower the dose to 25mg. This is the lowest recommended dose.
If you experience significant side effects: Stop taking Viagra and contact your doctor immediately. Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. Your doctor can adjust the dosage or suggest alternative treatments.
Consistency matters: Regularly discuss your response to Viagra with your doctor. They can help you determine the most appropriate and safe dosage based on your individual needs and health status.
Viagra Dosage and Interactions with Other Medications
The recommended starting dose of Viagra is 50mg taken orally about an hour before sexual activity. Your doctor might adjust this based on your response and health status. Never exceed 100mg in a 24-hour period.
Medications Affecting Viagra’s Effectiveness
Several medications can interact with Viagra, potentially reducing its effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. These include nitrates (used for chest pain), alpha-blockers (for high blood pressure or prostate problems), and some antifungal medications. Always inform your doctor of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting Viagra.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
Combining Viagra with nitrates can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Concomitant use of alpha-blockers can lead to dizziness or fainting. Some antifungal medications can increase Viagra’s concentration in your blood, potentially intensifying side effects. Your doctor can help manage these interactions and find a suitable alternative if needed. Common Viagra side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. Report any concerning side effects immediately.
Specific Medication Interactions
Ritonavir and Saquinavir (HIV protease inhibitors): These medications significantly increase Viagra’s levels in the blood, requiring a dose reduction or avoidance of Viagra altogether. Erythromycin and Ketoconazole (antibiotics and antifungals): Similar to ritonavir and saquinavir, these can boost Viagra levels, demanding careful monitoring. Always consult your doctor before combining Viagra with other medications. They will assess potential risks and make the best recommendation for your individual situation.