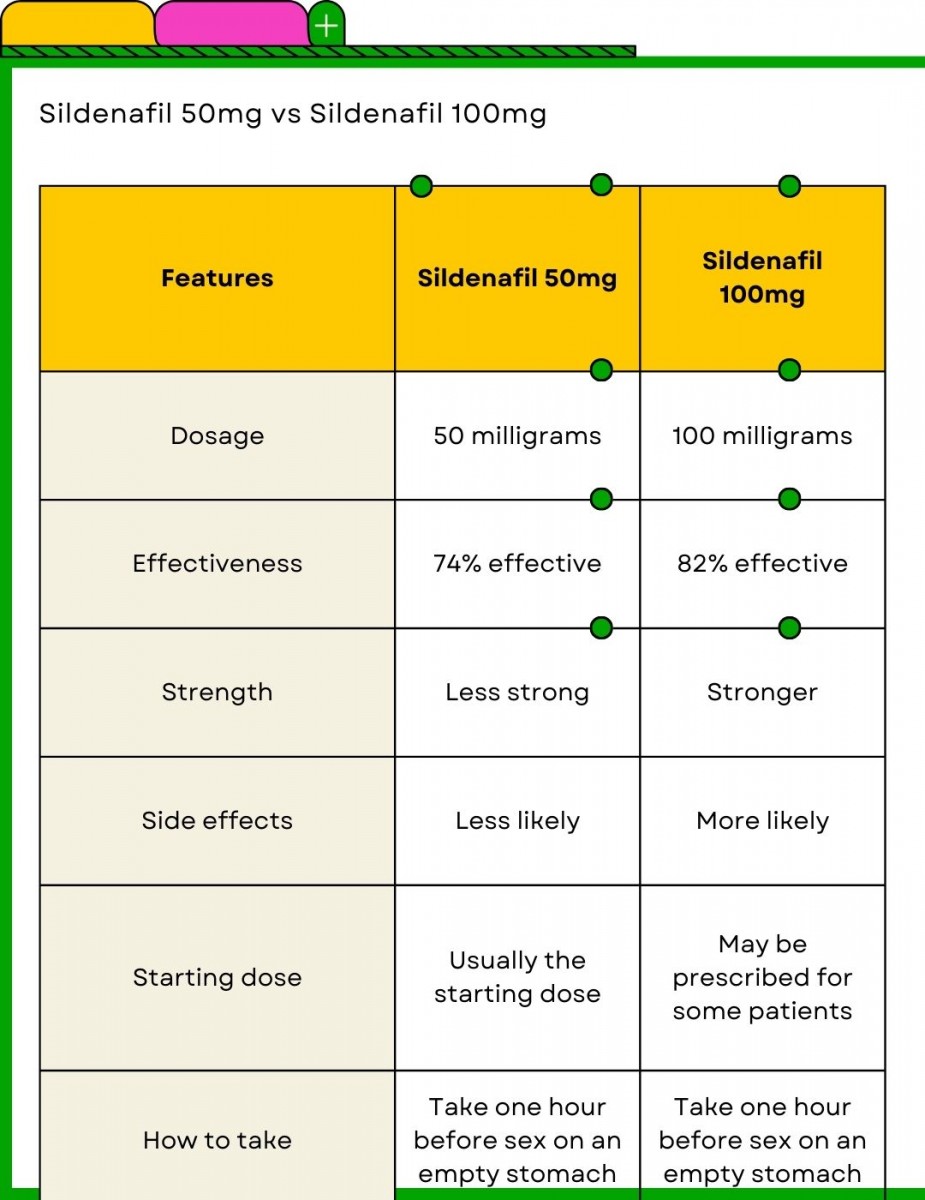
The typical starting dose for Viagra is 50mg, taken as needed, about an hour before sexual activity. Individual responses vary, however, so your doctor might adjust this based on your needs and health.
If 50mg proves insufficient, your doctor may increase it to 100mg. However, the maximum recommended dose is 100mg per day. Exceeding this can increase the risk of side effects.
Conversely, if you experience significant side effects at 50mg, a lower dose of 25mg might be more suitable. Remember, always consult your physician before adjusting your dosage.
Factors influencing dosage include your age, overall health, other medications you’re taking, and the severity of your erectile dysfunction. Open communication with your doctor is key to finding the right dose for you.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Schedule an appointment with your doctor to discuss Viagra and determine the appropriate dosage for your specific situation.
- Viagra Dose for Erectile Dysfunction
- Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
- Standard Viagra Dosage Recommendations
- Adjusting Your Dose
- Adjusting Viagra Dosage Based on Individual Needs
- Factors Influencing Dosage
- Dosage Adjustments
- Important Considerations
- Seeking Medical Advice
- Viagra Dosage and Pre-existing Health Conditions
- Heart Conditions
- Eye Conditions
- Blood Disorders
- Other Conditions
- Potential Side Effects and Dosage Considerations
- Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
- Specific Medication Interactions
- Substances to Avoid
- When to Consult a Doctor about Viagra Dosage
Viagra Dose for Erectile Dysfunction
The typical starting dose of Viagra is 50mg, taken as needed, about one hour before sexual activity.
Your doctor might recommend a lower dose of 25mg if you’re older than 65, have liver or kidney problems, or are taking certain medications.
Conversely, if 50mg isn’t effective, your doctor may increase the dose to 100mg. However, this shouldn’t exceed 100mg in a 24-hour period.
Remember, Viagra’s effectiveness varies between individuals. Factors like your overall health, age, and the specific cause of your erectile dysfunction play a role. Regular follow-up appointments with your doctor are vital to adjust your dosage and address any concerns.
Never exceed the prescribed dosage without consulting your physician. Taking more Viagra than recommended won’t necessarily improve results and could increase your risk of side effects.
Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. Report any unusual side effects to your doctor immediately.
This information is for guidance only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always discuss your treatment plan with your doctor before starting or changing any medication.
Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
Viagra, or sildenafil, primarily works by inhibiting an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). This enzyme breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a crucial molecule for achieving and maintaining an erection.
By blocking PDE5, Viagra allows cGMP levels to rise. Increased cGMP relaxes the smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis, increasing blood flow. This increased blood flow is what produces an erection.
The process begins with sexual stimulation, which triggers the release of nitric oxide. Nitric oxide then activates an enzyme that increases cGMP production. Viagra’s action enhances this natural process, making it more effective.
It’s important to note that Viagra doesn’t directly cause erections; it facilitates them by enhancing the body’s natural response to sexual stimulation. Sexual stimulation remains a necessary prerequisite for Viagra to work.
This mechanism explains why Viagra is only effective for men with erectile dysfunction caused by vascular issues. It won’t treat erectile dysfunction stemming from other underlying conditions, such as neurological problems or hormonal imbalances.
Standard Viagra Dosage Recommendations
The typical starting dose of Viagra is 50 mg, taken as needed, about one hour before sexual activity. This dose works well for many men.
Adjusting Your Dose
Your doctor may adjust your dose based on your response and individual needs. A lower dose of 25 mg might be prescribed if you experience side effects or if 50 mg proves too strong. Conversely, if 50 mg is insufficient, your doctor might increase it to 100 mg. However, this should only be done under strict medical supervision, as higher doses increase the risk of side effects.
Remember, never exceed the maximum recommended dose of 100 mg in a 24-hour period. Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and frequency.
Viagra’s effects can be influenced by factors like food and alcohol consumption. Your doctor will provide guidance on these aspects to optimize your treatment.
Adjusting Viagra Dosage Based on Individual Needs
Begin with the lowest recommended dose of 25mg. This allows your body to adjust and helps minimize potential side effects.
Factors Influencing Dosage
- Your age: Older men may require a lower starting dose.
- Liver or kidney function: Impaired function may necessitate dose reduction.
- Other medications: Certain drugs can interact with Viagra, possibly requiring dosage adjustments or alternative treatment.
- Overall health: Pre-existing conditions can influence how your body responds to Viagra.
Your doctor will consider these factors when determining your initial dose.
Dosage Adjustments
If 25mg proves insufficient, your doctor may increase the dose to 50mg. The maximum recommended dose is 100mg. However, increasing the dose doesn’t guarantee better results and may increase side effects.
- Insufficient Response: If 25mg is ineffective, discuss a dose increase with your doctor. They will assess your response and adjust accordingly.
- Side Effects: If you experience undesirable side effects, such as headaches, flushing, or visual disturbances, your doctor may recommend a lower dose or an alternative treatment. Never adjust your dosage without consulting your physician.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups allow your doctor to monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments based on your response and overall health.
Important Considerations
- Viagra is not suitable for everyone. It’s crucial to discuss your medical history with your doctor before starting treatment.
- Do not take more than one Viagra tablet per day.
- Always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely.
Seeking Medical Advice
Remember, this information is for general knowledge only. Always consult your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding Viagra dosage and treatment for erectile dysfunction. They can provide the most appropriate treatment plan based on your unique needs and health profile.
Viagra Dosage and Pre-existing Health Conditions
Always discuss your medical history with your doctor before starting Viagra. Your pre-existing conditions significantly influence the appropriate Viagra dosage, and in some cases, may prohibit its use altogether. For example, patients with severe heart conditions may need a lower starting dose or an alternative treatment. Those with liver or kidney disease might require dosage adjustments due to altered drug metabolism.
Heart Conditions
Individuals with a history of heart attacks, unstable angina, or uncontrolled high blood pressure should exercise extreme caution. Viagra can lower blood pressure, potentially exacerbating these conditions. Your doctor will carefully assess your risk and determine a safe starting dose, if any.
Eye Conditions
Rarely, Viagra can cause vision changes. If you have a pre-existing eye condition like retinitis pigmentosa, discuss this with your doctor before using Viagra, as it could worsen the condition.
Blood Disorders
Patients with bleeding disorders or a predisposition to them should use Viagra with caution. Viagra can increase the risk of bleeding.
Other Conditions
Conditions like stomach ulcers, sickle cell anemia, leukemia, or multiple myeloma may also interact with Viagra. Your physician will consider these factors when prescribing the medication and determining the correct dosage.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Potential Side Effects and Dosage Considerations
Always discuss Viagra dosage with your doctor. Starting with the lowest dose (25mg) is generally recommended. This minimizes potential side effects.
Common side effects include headache, facial flushing, nasal congestion, and indigestion. These are usually mild and temporary. However, some individuals experience more serious reactions.
- Serious Side Effects: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience chest pain, irregular heartbeat, sudden vision loss, or prolonged erection (priapism).
- Interactions: Viagra can interact negatively with certain medications, particularly nitrates. Inform your doctor about all medications you are currently taking.
- Dosage Adjustment: Your doctor may adjust your dose based on your response and any side effects. Increasing the dose beyond the recommended maximum (100mg) is not advised.
Factors influencing dosage include your overall health, age, and the severity of your erectile dysfunction. Some conditions may necessitate a lower starting dose or a different treatment altogether.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Heart problems, liver or kidney disease, and low blood pressure require careful monitoring and potentially lower doses.
- Other Medications: Certain medications can interact with Viagra, impacting its effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. Always disclose your full medication history to your physician.
- Age: Older men may require a lower starting dose due to reduced liver and kidney function.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before starting or changing any medication.
Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal supplements, and recreational drugs. Certain medications can significantly affect Viagra’s effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects. This includes nitrates, used to treat chest pain (angina). Combining them can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Alpha-blockers, often prescribed for high blood pressure or prostate problems, can also interact negatively, potentially leading to dizziness or fainting.
Specific Medication Interactions
Nitrates: Avoid Viagra if you use any form of nitrates. This includes nitroglycerin, isosorbide dinitrate, and isosorbide mononitrate.
Alpha-blockers: Your doctor may need to adjust your Viagra dose or prescribe an alternative if you take alpha-blockers. Common alpha-blockers include terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, and alfuzosin.
CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Medications that inhibit the CYP3A4 enzyme, like ketoconazole and ritonavir, can increase Viagra’s concentration in your blood, potentially enhancing side effects. Your doctor might lower your Viagra dose.
CYP3A4 Inducers: Conversely, medications like rifampin and St. John’s Wort can decrease Viagra’s effectiveness by speeding up its metabolism.
Substances to Avoid
Alcohol can worsen Viagra’s side effects, including dizziness and headache. Grapefruit juice also interacts with Viagra’s metabolism, potentially leading to increased blood levels and side effects. Avoid excessive alcohol consumption and grapefruit juice while taking Viagra. Recreational drugs, especially those affecting blood pressure or heart rate, should be avoided while on Viagra. Discuss any substance use with your doctor before taking Viagra.
When to Consult a Doctor about Viagra Dosage
Schedule a doctor’s appointment if Viagra doesn’t improve your erectile dysfunction or causes side effects. This is crucial for personalized advice.
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience chest pain, irregular heartbeat, or vision changes while using Viagra. These are serious potential side effects requiring prompt medical evaluation.
Consult your physician if you have pre-existing conditions like heart disease, low blood pressure, or bleeding disorders. They can assess your suitability for Viagra and determine the appropriate dosage.
If you’re taking other medications, especially nitrates, discuss this with your doctor before starting Viagra. Drug interactions can be dangerous.
Adjustments to your Viagra dosage might be necessary based on your response to treatment. Your doctor can help you find the most effective dose.
| Symptom | Action |
|---|---|
| No improvement in ED | Consult your doctor for dosage adjustment or alternative treatment options. |
| Side effects (headache, flushing, etc.) | Discuss these with your doctor; they may suggest a lower dose or an alternative. |
| Severe side effects (chest pain, vision changes) | Seek immediate medical attention. |
| Pre-existing health conditions | Inform your doctor before starting Viagra. |
| Interaction with other medications | Always disclose all medications you are taking to your doctor. |
Regular check-ups with your doctor, particularly if you are on long-term Viagra treatment, ensure your health and the medication’s efficacy are monitored.