Need help understanding Viagra and similar medications? Focus on Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors. These drugs, including Viagra (sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), and Levitra (vardenafil), address erectile dysfunction by increasing blood flow to the penis.
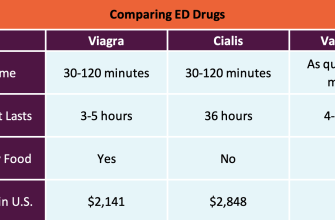
Each medication offers a slightly different duration of action. Viagra typically lasts 4-5 hours, while Cialis can provide effects for up to 36 hours. Levitra’s duration is generally between 4 and 6 hours. Dosage varies depending on individual needs and medical history; always consult a doctor for personalized advice.
Important Note: PDE5 inhibitors are not suitable for everyone. Pre-existing health conditions, such as heart problems or low blood pressure, may contraindicate their use. Interactions with other medications are also a serious consideration. Always disclose your complete medical history to your physician before starting any treatment.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Seek professional medical guidance for diagnosis and treatment of erectile dysfunction or any related health concerns. Never self-medicate.
- Viagra: A Detailed Look at the Drug
- What is Viagra (Sildenafil)?
- How Viagra Works
- Important Considerations
- Alternative Treatments
- How Viagra Works: The Mechanism of Action
- Increased cGMP: The Key to Erection
- Beyond PDE5 Inhibition: Other Effects
- Viagra’s Uses and Indications
- Common Side Effects of Viagra
- Serious Side Effects and Precautions
- Cardiovascular Risks
- Other Potential Side Effects
- Drug Interactions with Viagra
- Viagra Dosage and Administration
- Adjusting Your Dosage
- How to Take Viagra
- Alternatives to Viagra for Erectile Dysfunction
- Lifestyle Changes and Therapies
- Other Medications
- Vacuum Erection Devices (VEDs)
- Penile Implants
- Comparison of Treatment Options
- Choosing the Right Treatment
- Viagra and its Cost: Accessibility and Affordability
Viagra: A Detailed Look at the Drug
Viagra, or sildenafil citrate, is a medication primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). It works by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection.
Here’s what you should know:
- Mechanism of Action: Viagra inhibits an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5), leading to increased levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). Higher cGMP levels relax blood vessels, allowing for improved blood flow.
- Dosage: The typical starting dose is 50mg, taken as needed, approximately one hour before sexual activity. Your doctor may adjust this based on your response and health status. Never exceed the recommended dosage.
- Side Effects: Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. More serious, though rare, side effects include sudden vision loss or hearing loss. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these.
- Precautions: Viagra is not suitable for everyone. Individuals with heart conditions, low blood pressure, or certain eye problems should discuss its use with their physician. It also interacts with some medications, like nitrates.
- Alternatives: Other medications for ED include tadalafil (Cialis) and vardenafil (Levitra). Your doctor can help determine the best option for you.
Before taking Viagra, consult your doctor for a thorough assessment to ensure it’s the right choice for you and to discuss potential risks and benefits. They can guide you on safe usage and help manage potential side effects.
- Schedule a consultation with your doctor to discuss your health history and any medications you’re currently taking.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and timing.
- Report any side effects to your doctor immediately.
- Store Viagra properly to maintain its efficacy.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication.
What is Viagra (Sildenafil)?
Viagra, containing the active ingredient sildenafil, is a medication primarily used to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. It works by increasing blood flow to the penis, helping to achieve and maintain an erection.
How Viagra Works
Sildenafil inhibits an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). This allows increased levels of cyclic GMP, a molecule that relaxes blood vessel muscles. The resulting increased blood flow facilitates an erection in response to sexual stimulation.
Important Considerations
Viagra is not a hormone or a stimulant; it only works with sexual stimulation. It’s crucial to discuss your health history with a doctor before starting Viagra, especially if you have heart problems, low blood pressure, or take certain other medications. Common side effects include headaches, facial flushing, and nasal congestion. Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and usage.
Alternative Treatments
Other medications for ED exist, including tadalafil (Cialis) and vardenafil (Levitra). Your doctor can help determine the best treatment option based on your individual needs and health status. Lifestyle changes like exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management can also contribute to improved sexual health.
How Viagra Works: The Mechanism of Action
Viagra, or sildenafil, primarily targets an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). PDE5 breaks down a crucial messenger molecule, cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which plays a vital role in penile erection. By inhibiting PDE5, Viagra increases cGMP levels.
Increased cGMP: The Key to Erection
Higher cGMP levels trigger relaxation of smooth muscles in the penis’s blood vessels. This relaxation allows increased blood flow into the corpora cavernosa, the spongy tissue responsible for erection. This increased blood flow leads to engorgement and, subsequently, an erection.
Importantly, Viagra only works in the presence of sexual stimulation. It doesn’t spontaneously cause erections; it enhances the body’s natural response to sexual arousal by facilitating the necessary blood flow.
Beyond PDE5 Inhibition: Other Effects
While PDE5 inhibition is the primary mechanism, Viagra also interacts with other pathways in the body. It’s important to consult a doctor before using Viagra, as these interactions can influence its effect and potential side effects. Individual responses vary, and appropriate dosage is critical for safety and efficacy.
Viagra’s Uses and Indications
Viagra, or sildenafil citrate, primarily treats erectile dysfunction (ED) in men. It works by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection.
Beyond ED, Viagra finds application in treating pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). This condition involves high blood pressure in the arteries leading to the lungs. Viagra helps relax and widen these blood vessels, improving blood flow.
| Condition | Mechanism of Action | Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Erectile Dysfunction | Increases blood flow to the penis | Typically 50mg, can be adjusted |
| Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension | Relaxes and widens blood vessels in the lungs | Dosage varies significantly; prescribed by a physician |
Always consult your doctor before using Viagra. They can determine if it’s appropriate for your health status and prescribe the correct dosage. Remember, self-medicating can be risky.
Viagra interacts with certain medications. Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you take. This information is crucial for safe and effective treatment.
Potential side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. Your doctor can discuss these potential side effects with you in more detail.
Common Side Effects of Viagra
Viagra, while effective for many, can cause side effects. Understanding these is key to safe usage.
- Headache: This is a frequent side effect, often mild and temporary. Drink plenty of water and consider over-the-counter pain relief if needed.
- Facial Flushing: Your face may feel warm or red. This usually subsides on its own.
- Indigestion: Some men experience heartburn or upset stomach. Avoid large meals before taking Viagra.
- Nasal Congestion: A stuffy or runny nose is possible. Use saline nasal spray if necessary.
- Visual Disturbances: Temporary changes in vision, like blurred vision or sensitivity to light, may occur. These usually resolve quickly.
- Muscle Aches: Minor muscle pain is another potential side effect. Rest and light exercise can help.
Less common, but still possible side effects include:
- Dizziness
- Back Pain
- Hearing problems
Serious side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention. These include chest pain, prolonged erection (priapism), sudden vision loss, or hearing loss. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience any of these.
Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and frequency. Open communication with your physician is vital for addressing any concerns or managing side effects.
- Discuss your medical history thoroughly with your doctor before starting Viagra.
- Report any concerning side effects promptly to your doctor.
- Avoid alcohol consumption while taking Viagra, as it can worsen some side effects.
Serious Side Effects and Precautions
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience sudden vision loss, chest pain, irregular heartbeat, or prolonged erection (lasting more than four hours). These are serious side effects requiring prompt medical intervention.
Cardiovascular Risks
Viagra and similar medications can lower blood pressure. If you have heart disease, high blood pressure, or have recently had a stroke or heart attack, discuss the risks with your doctor before using this medication. Using Viagra with nitrates can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Avoid combining them.
Other Potential Side Effects
Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and upset stomach. Less common, but still possible, are dizziness, visual disturbances (besides vision loss), and hearing problems. Inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including herbal supplements, as interactions can occur. Proper dosage and medical oversight are paramount to minimizing risks. Do not increase the dosage without consulting a physician. Regular check-ups are highly recommended during treatment.
Drug Interactions with Viagra
Always inform your doctor about all medications you take, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, before starting Viagra. This includes nitrates, often prescribed for chest pain. Combining Viagra with nitrates can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure.
Alpha-blockers, commonly used to treat high blood pressure and enlarged prostate, can also interact with Viagra, potentially leading to low blood pressure. Your doctor may need to adjust your dosage.
Certain antifungal medications, such as ketoconazole and itraconazole, can increase Viagra’s levels in your blood, potentially causing side effects. Your doctor may suggest a lower Viagra dose.
Drugs used to treat HIV/AIDS, such as ritonavir and indinavir, can similarly elevate Viagra’s concentration, necessitating careful monitoring and potential dose adjustments.
Some antidepressants, particularly those classified as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can interact with Viagra and impact its effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects. Open communication with your doctor is paramount.
Grapefruit juice inhibits enzymes that metabolize Viagra, leading to increased drug levels and potential side effects. Avoid grapefruit juice while taking Viagra.
This information is not exhaustive. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for a complete list of potential interactions and personalized advice. Your health is your priority, and a frank discussion about your medications is crucial.
Viagra Dosage and Administration
The recommended starting dose of Viagra is 50 mg taken as needed, approximately one hour before sexual activity. This dose can be increased to 100 mg or decreased to 25 mg, depending on individual response and tolerance. Never exceed 100 mg in a 24-hour period.
Adjusting Your Dosage
Your doctor will help you determine the appropriate dose based on your health status and other medications you’re taking. Factors such as age, liver or kidney function, and the presence of other health conditions influence optimal dosage. They will guide you through the process of finding the right amount for your needs. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
How to Take Viagra
Take Viagra orally with a glass of water. It can be taken with or without food, but taking it on an empty stomach may lead to faster absorption. Avoid excessive alcohol consumption before or while taking Viagra, as it may reduce its effectiveness and increase the risk of side effects.
Remember to discuss any potential drug interactions with your physician before starting Viagra. They can advise you on potential incompatibilities and ensure your safety.
Alternatives to Viagra for Erectile Dysfunction
Consider exploring other treatment options. Many effective alternatives exist.
Lifestyle Changes and Therapies
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques like yoga or meditation can significantly improve erectile function. These lifestyle adjustments often enhance overall health and contribute to better sexual performance. Additionally, counseling can address underlying psychological factors contributing to ED.
Other Medications
Your doctor might prescribe alternative oral medications like tadalafil (Cialis) or avanafil (Stendra), each with slightly different properties and durations of action. These drugs work similarly to Viagra but may be more suitable depending on individual needs and preferences. Another option includes injections of alprostadil directly into the penis, providing a quick and effective solution.
Vacuum Erection Devices (VEDs)
VEDs are non-invasive devices creating an erection by increasing blood flow to the penis. They are a safe and effective option for many men, often used independently or in conjunction with other treatments.
Penile Implants
For men who haven’t found success with other methods, a penile implant is a surgical option offering a permanent solution. This involves surgically placing inflatable or malleable rods within the penis to provide rigidity.
Comparison of Treatment Options
| Treatment | Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Medications (Cialis, Stendra) | Increases blood flow | Easy to use, relatively long-lasting effects | Side effects possible, may not be suitable for all |
| Alprostadil Injections | Directly relaxes penile muscles | Fast acting, effective | Requires injection, potential for bruising or pain |
| VEDs | Increases blood flow mechanically | Non-invasive, relatively inexpensive | Requires some manual dexterity, may not be comfortable for all |
| Penile Implants | Provides permanent rigidity | Permanent solution | Surgical procedure, potential complications |
Choosing the Right Treatment
Consultation with a doctor is crucial to determine the best approach. A thorough medical history review and physical examination help identify the underlying cause of ED and select the most appropriate and safe treatment strategy. They’ll discuss the benefits and risks of each option to help you make an informed decision.
Viagra and its Cost: Accessibility and Affordability
Consider generic sildenafil, the active ingredient in Viagra. It significantly reduces the cost compared to the branded medication.
Factors influencing Viagra’s price include:
- Brand name vs. generic: Generic sildenafil is considerably cheaper.
- Dosage: Higher dosages typically cost more.
- Pharmacy: Prices vary between pharmacies; online pharmacies often offer competitive pricing, but verify legitimacy.
- Insurance coverage: Check with your insurance provider; some plans cover erectile dysfunction medication.
- Location: Prices differ geographically.
To find the best price:
- Compare prices: Use online pharmacy comparison websites (ensure they’re reputable).
- Check for coupons or discounts: Many pharmacies offer savings programs.
- Negotiate with your pharmacy: Inquire about discounts or payment plans.
- Explore patient assistance programs: Pharmaceutical companies sometimes offer programs to help patients afford medications.
Remember to consult your doctor before starting any medication, including Viagra or generic sildenafil, to discuss potential side effects and drug interactions. Your doctor can also advise on suitable dosages and help you navigate cost-effective options.