Need help with erectile dysfunction? Consider consulting a doctor to discuss Viagra. This medication can significantly improve your sexual health, but it’s crucial to understand its proper usage and potential side effects.
Viagra, or sildenafil, works by increasing blood flow to the penis, facilitating an erection. Dosage typically ranges from 25mg to 100mg, with your doctor determining the appropriate amount based on your individual needs and health history. Remember, never exceed the prescribed dose.
Common side effects include headaches, flushing, and nasal congestion. More serious, though rare, side effects include vision changes and prolonged erections (priapism). Report any concerning symptoms to your physician immediately. This medication interacts with certain other drugs, so provide your doctor with a complete list of your current medications.
Viagra isn’t a cure for ED; it addresses the symptoms. Lifestyle changes, like regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management, can complement medication and improve overall sexual function. Open communication with your partner is also key to a fulfilling sex life.
Remember: Viagra is a prescription medication. Obtain it only from a licensed healthcare professional. Self-medicating can be dangerous. A thorough medical evaluation will ensure the medication is suitable for you and that potential risks are minimized. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor any questions you may have.
- Use of Viagra for Men
- What is Viagra and How Does it Work?
- Understanding the Mechanism
- Viagra’s Effectiveness and Potential Side Effects
- Factors Influencing Viagra’s Success
- Common Side Effects
- Who Should and Shouldn’t Use Viagra?
- Who Should Consider Viagra?
- Who Shouldn’t Use Viagra?
- How to Take Viagra Safely and Effectively
- Viagra and Other Erectile Dysfunction Treatments: A Comparison
- Potential Interactions with Other Medications
- Specific Medication Groups to Note
- Cost and Accessibility of Viagra
- Long-Term Use and Potential Health Concerns
Use of Viagra for Men
Consult your doctor before using Viagra. He can assess your overall health and determine if Viagra is appropriate for you, considering any pre-existing conditions or medications you are taking. This is crucial for safe and effective use.
Viagra, containing sildenafil, enhances blood flow to the penis, aiding in achieving an erection. It’s designed for erectile dysfunction treatment, not enhancement in men who don’t experience this issue.
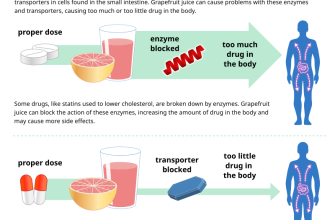
Take Viagra as prescribed. The typical dose is 50mg, but your doctor may adjust this based on your individual response and health. Avoid consuming grapefruit or grapefruit juice, as it can interfere with Viagra’s metabolism.
Common side effects include headaches, flushing, and nasal congestion. More serious side effects, though rare, include vision changes and chest pain. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these.
Viagra isn’t suitable for everyone. Men with heart conditions, low blood pressure, or certain eye problems should discuss potential risks with their doctor before use. Also, inform your doctor about any other medications you’re taking, to avoid potential interactions.
Alcohol consumption can reduce Viagra’s effectiveness and increase the risk of side effects. Moderate alcohol intake is recommended, if any.
Remember: This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always discuss your treatment options with a healthcare provider.
Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional before using any medication.
What is Viagra and How Does it Work?
Viagra, the brand name for sildenafil citrate, is a medication prescribed to treat erectile dysfunction (ED). It works by increasing blood flow to the penis. This increased blood flow allows for a firmer erection when sexually stimulated.
Understanding the Mechanism
Specifically, Viagra inhibits an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). PDE5 normally breaks down a molecule called cyclic GMP, which is crucial for achieving and maintaining an erection. By blocking PDE5, Viagra allows cyclic GMP levels to remain elevated, facilitating blood vessel relaxation and increased blood flow to the penis.
It’s important to note that Viagra only works when sexual stimulation is present. It doesn’t create an erection on its own; it simply enhances the body’s natural response to sexual stimulation.
Viagra comes in different dosages, and your doctor will determine the appropriate dose based on your individual needs and health condition. Always follow your doctor’s instructions and consult them before starting or stopping any medication, including Viagra. They can help you understand the potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Viagra’s Effectiveness and Potential Side Effects
Viagra, or sildenafil citrate, helps many men achieve and maintain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual intercourse. Clinical trials show a success rate ranging from 60% to 80%, depending on dosage and individual factors like overall health and the cause of erectile dysfunction.
Factors Influencing Viagra’s Success
Success rates vary. Proper dosage, consistent adherence to medical guidance, and addressing underlying health conditions are crucial. Some men may need higher doses or alternative treatments. Diet and lifestyle can also influence results.
| Factor | Impact on Viagra’s Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Dosage | Higher doses generally lead to better results, but come with increased side effect risk. |
| Underlying health conditions | Conditions like diabetes or heart disease can affect response. |
| Lifestyle | Smoking, excessive alcohol, and lack of exercise can reduce efficacy. |
Common Side Effects
Viagra can cause side effects. The most common are headache, facial flushing, nasal congestion, and upset stomach. Less frequently, visual disturbances (blurred vision, sensitivity to light) and muscle aches can occur. Rarely, more serious side effects such as prolonged erections (priapism) or hearing loss can develop. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these.
Always discuss potential side effects and interactions with your doctor before starting Viagra or any other medication. They can help you manage risks and determine the best course of treatment.
Who Should and Shouldn’t Use Viagra?
Viagra, or sildenafil, is a medication for erectile dysfunction (ED), but it’s not for everyone. Men who experience ED should consult their doctor to determine if Viagra is a suitable treatment option.
Who Should Consider Viagra?
- Men with ED who haven’t found success with other treatments or lifestyle changes.
- Men whose ED significantly impacts their quality of life and relationships.
- Men whose doctor has ruled out other underlying medical conditions causing ED.
- Men aged 18 and older who meet the necessary health criteria.
Your doctor will assess your overall health and medical history before prescribing Viagra. This includes reviewing current medications and identifying potential interactions.
Who Shouldn’t Use Viagra?
- Men with heart conditions, uncontrolled high blood pressure, or a history of heart attack or stroke. Viagra can place added strain on the heart.
- Men taking nitrates for chest pain. Combining nitrates and Viagra can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure.
- Men with severe liver or kidney problems. Viagra’s metabolism and elimination may be affected.
- Men with certain eye conditions, such as retinitis pigmentosa.
- Men with a history of priapism (prolonged erection).
- Men taking certain medications, including some antifungals and antibiotics. Drug interactions can occur.
It’s crucial to have an open and honest discussion with your doctor about your medical history and any medications you’re taking. They can accurately assess your suitability for Viagra and discuss potential risks and benefits.
Remember: This information is for general knowledge and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
How to Take Viagra Safely and Effectively
Take Viagra exactly as your doctor prescribes. The usual starting dose is 50mg, taken about an hour before sexual activity.
Dosage Adjustments: Your doctor may adjust your dose based on your response and any side effects. Never exceed the recommended dose without consulting your physician. Don’t take more than one tablet in 24 hours.
Food and Alcohol: Fatty meals can delay Viagra’s onset. Limit alcohol consumption as it can interact negatively with the medication and increase the risk of side effects.
Side Effects: Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. If you experience severe or persistent side effects, contact your doctor immediately.
Medical Conditions: Inform your doctor of all your medical conditions, including heart problems, low blood pressure, or liver/kidney disease, before taking Viagra. Certain medications can also interact negatively with Viagra.
Contraindications: Viagra is not suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain heart conditions, or those taking specific medications (like nitrates), should avoid Viagra.
Storage: Store Viagra in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep it out of reach of children.
Consult Your Doctor: If you have questions or concerns about Viagra, or if you experience unexpected symptoms, consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance.
Viagra and Other Erectile Dysfunction Treatments: A Comparison
Choosing the right erectile dysfunction (ED) treatment depends on individual needs and preferences. Viagra (sildenafil) is a popular choice, but several other options exist.
- Viagra (Sildenafil): Acts by increasing blood flow to the penis. Onset is typically 30-60 minutes. Side effects can include headache, flushing, and nasal congestion. It’s not suitable for everyone, particularly those with heart conditions or taking certain medications.
- Cialis (Tadalafil): Similar to Viagra, but its effects last much longer (up to 36 hours), earning it the nickname “weekend pill.” This extended duration can be advantageous for some men. Side effects are comparable to Viagra.
- Levitra (Vardenafil): Another PDE5 inhibitor, similar in action to Viagra and Cialis. It may offer a faster onset of action for some individuals. Side effects are also similar.
- Avanafil (Stendra): A newer PDE5 inhibitor with a relatively fast onset of action (15-30 minutes). Side effects are generally similar to other PDE5 inhibitors.
Beyond oral medications, other treatment options include:
- Penile injections: These injections directly introduce medication into the penis, causing immediate erection. This is generally used for specific situations or when other treatments haven’t worked. Side effects can include pain and bruising.
- Vacuum erection devices (VEDs): These devices create a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood in and causing an erection. They’re generally a non-invasive option, although some men may find them cumbersome.
- Penile implants: A surgical option involving the insertion of inflatable or malleable rods into the penis to provide a permanent solution for ED. This is usually considered a last resort.
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management are crucial for overall health and can positively impact erectile function. Addressing underlying conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure is also important.
- Consult your doctor: Before starting any ED treatment, a thorough medical examination is necessary to determine the underlying cause of ED and assess your suitability for specific treatments. Your doctor can help you weigh the risks and benefits of each option and guide you towards the most appropriate course of action.
- Discuss side effects: Openly discuss potential side effects with your physician. This ensures you are adequately informed and can manage any side effects effectively.
- Consider your lifestyle: Factor your lifestyle and preferences into your decision. For instance, if spontaneity is important, Cialis might be preferable to Viagra.
Remember, effective treatment for ED often involves a combination of approaches, and what works best varies significantly between individuals.
Potential Interactions with Other Medications
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies, before starting Viagra. This includes nitrates, often used for chest pain. Combining Viagra with nitrates can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure.
Specific Medication Groups to Note
Certain medications interact negatively with Viagra. Alpha-blockers, used to treat high blood pressure and enlarged prostate, can increase the risk of low blood pressure when taken with Viagra. Similarly, some antifungals and HIV protease inhibitors may affect Viagra’s metabolism, potentially altering its effectiveness or increasing side effects. Blood thinners can also increase the risk of bleeding when used with Viagra.
Discuss potential interactions with your physician. They can help you assess the risks and benefits and recommend appropriate alternatives if necessary. Never adjust your medication dosage without consulting your doctor. Your health is paramount, and open communication with your healthcare provider is key.
Cost and Accessibility of Viagra
Viagra’s price varies significantly depending on your location, insurance coverage, and the pharmacy you choose. Generic versions, such as sildenafil, are considerably cheaper than branded Viagra. Expect to pay anywhere from $20 to $80 per pill for brand-name Viagra, while generic sildenafil might cost between $1 and $15 per pill, depending on dosage and quantity purchased.
Many pharmacies offer discounts or coupons, and online pharmacies sometimes provide lower prices. However, always verify the legitimacy of any online pharmacy before making a purchase to avoid counterfeit drugs. Consider comparing prices from multiple sources.
Insurance coverage can drastically reduce the out-of-pocket cost. Check with your provider to see if Viagra or sildenafil is covered under your plan. Depending on your policy, you might only need a small co-pay.
For men without insurance or facing high costs, patient assistance programs offered by pharmaceutical companies may help. These programs provide medication at reduced or no cost to eligible individuals. Research available options based on your income and circumstances.
Accessibility also involves ease of obtaining the medication. While Viagra and its generics are widely available through traditional pharmacies, online pharmacies offer another access point. Remember, though, to consult your doctor before starting any treatment and to prioritize reputable sources for purchasing medication.
Long-Term Use and Potential Health Concerns
Consult your doctor before starting long-term Viagra use. Regular checkups are vital for monitoring your health and adjusting medication as needed.
Prolonged Viagra use can potentially lead to hearing loss, vision problems such as blue-tinged vision or sudden vision loss, and heart-related issues including chest pain or irregular heartbeat. These are serious risks, requiring immediate medical attention.
Priapism, a persistent, painful erection lasting more than four hours, is a rare but serious side effect. Seek immediate medical help if this occurs; untreated priapism can cause permanent damage.
Blood pressure is also impacted. Viagra can lower blood pressure, potentially interacting negatively with nitrates or certain heart medications. Always disclose all medications to your physician.
Long-term use might increase the chance of developing nausea, headaches, flushing, and indigestion. These side effects are generally mild, but persistent issues warrant a doctor’s visit.
Liver and kidney function should be closely monitored, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions. Viagra metabolism can stress these organs.
Remember, individual responses vary. Your doctor will assess your specific health status and advise on the appropriate course of action regarding long-term Viagra usage or potential alternative treatments.