Always consult your doctor before combining Viagra (sildenafil) with other medications. This crucial step prevents dangerous interactions. Many prescription drugs can affect how Viagra works, or vice-versa, potentially causing serious side effects.
For instance, nitrates, commonly prescribed for chest pain, are strictly contraindicated with Viagra. This combination can lead to a dramatic drop in blood pressure, resulting in dizziness, fainting, and even heart attack. Alpha-blockers, often used to treat high blood pressure and enlarged prostate, can also interact, causing significant blood pressure fluctuations.
Certain antibiotics, antifungals, and HIV medications may affect Viagra’s efficacy or increase the risk of side effects. Specific examples include erythromycin, ketoconazole, and ritonavir. Your physician can assess your medication profile and determine the safest approach. Open communication about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, is paramount.
Remember, this information isn’t a substitute for professional medical advice. Your doctor possesses the necessary expertise to evaluate your unique health situation and provide personalized recommendations regarding Viagra and other medications. Schedule a consultation to discuss any concerns you have about potential drug interactions.
- Viagra and Prescription Drugs: A Detailed Overview
- Understanding Potential Drug Interactions
- Managing Medications Safely
- Specific Medication Classes and Viagra
- Disclaimer:
- Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
- Nitric Oxide’s Role
- Factors Affecting Viagra’s Action
- Individual Variability
- Common Prescription Drugs that Interact with Viagra
- Dangerous Combinations: Viagra and Nitrates
- Understanding the Risk
- What to Do
- Alternative Treatments
- Viagra and Blood Pressure Medications: Potential Risks and Precautions
- Understanding the Interaction
- Safe Practices
- Specific Blood Pressure Medication Considerations
- Each blood pressure medication interacts differently with Viagra. Your doctor will personalize your treatment plan based on your specific drugs and health status.
- Viagra and Antidepressants: Considerations for Concurrent Use
- Specific Antidepressant Interactions
- Managing Potential Risks
- Alternative Treatments
- Viagra and Alpha-Blockers: Managing Potential Side Effects
- Understanding the Interaction
- Minimizing Risks
- Managing Symptoms
- Dosage Considerations
- Seeking Medical Advice
- Alternative Treatments
- Viagra and Antifungal Medications: Important Interactions to Note
- Seeking Professional Guidance: Importance of Doctor Consultation
- Understanding Potential Interactions
- Personalized Treatment Plan
- Monitoring Your Progress
Viagra and Prescription Drugs: A Detailed Overview
Always consult your doctor before combining Viagra (sildenafil) with other medications. Many prescription drugs interact negatively with Viagra, potentially causing dangerous side effects. This includes nitrates, used to treat angina, which can lead to a drastic drop in blood pressure. Alpha-blockers, commonly prescribed for high blood pressure and prostate problems, can also interact adversely, resulting in dizziness and fainting.
Understanding Potential Drug Interactions
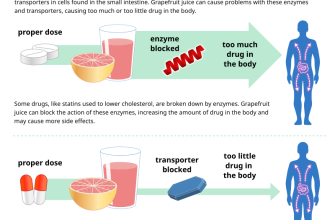
Specific examples of problematic drug interactions include those with certain antibiotics (like erythromycin), antifungals (like ketoconazole), and HIV protease inhibitors. These can increase Viagra’s concentration in the bloodstream, raising the risk of side effects. Conversely, some medications can reduce Viagra’s effectiveness. For instance, rifampin, an antibiotic, accelerates Viagra’s metabolism, decreasing its potency.
Managing Medications Safely
Before starting any new medication, including Viagra, provide your doctor with a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking. This allows them to assess potential interactions and adjust dosages or medications as needed. Open communication with your doctor is vital for safe and effective medication management. Never self-medicate or alter prescribed dosages without consulting your healthcare provider. Regular check-ups and honest disclosure of your medications are key to preventing adverse effects.
Specific Medication Classes and Viagra
Antidepressants: Some antidepressants, particularly SSRIs and SNRIs, can impact sexual function, sometimes necessitating the use of Viagra. However, careful monitoring is required due to potential interactions. Blood thinners: While not a direct contraindication, the combination of Viagra and blood thinners warrants careful consideration and medical supervision to minimize bleeding risk. Heart medications: As mentioned, several heart medications interact significantly with Viagra. Thorough evaluation of your cardiovascular health is crucial before starting Viagra therapy.
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment.
Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
Viagra, or sildenafil, works by inhibiting a specific enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). This enzyme normally breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), a crucial molecule involved in the penis’s erectile process.
By blocking PDE5, Viagra allows cGMP levels to increase. Higher cGMP levels relax the smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis, increasing blood flow. This increased blood flow leads to an erection.
Nitric Oxide’s Role
The process starts with nitric oxide (NO), a neurotransmitter released during sexual stimulation. NO triggers a cascade of events leading to increased cGMP. Viagra enhances this process by preventing cGMP breakdown, thus amplifying the effects of NO.
Factors Affecting Viagra’s Action
Several factors influence how effectively Viagra works. These include the patient’s overall health, pre-existing conditions like heart disease, and interactions with other medications. Always consult your physician before using Viagra.
| Factor | Effect on Viagra |
|---|---|
| Heart Disease | May increase risk; careful monitoring needed. |
| Liver or Kidney Disease | May affect metabolism and dosage requirements. |
| Nitrate Medications | Dangerous interaction; strictly contraindicated. |
Individual Variability
Response to Viagra varies among individuals. Some may experience a stronger effect than others. It’s a personalized response related to various factors including age, genetics and overall health.
Common Prescription Drugs that Interact with Viagra
Always discuss potential interactions with your doctor before combining Viagra with other medications. Here’s a list of drug classes known to interact:
- Nitrates: Nitroglycerin, isosorbide mononitrate, and other nitrates used to treat angina (chest pain) can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure when taken with Viagra. This combination can lead to serious, even life-threatening consequences.
- Alpha-blockers: These medications, often prescribed for high blood pressure or enlarged prostate, can also lower blood pressure, increasing the risk of dizziness and fainting when combined with Viagra.
- CYP3A4 inhibitors: Some medications, such as ketoconazole (antifungal), erythromycin (antibiotic), and ritonavir (HIV medication), inhibit the enzyme that breaks down Viagra. This can lead to higher Viagra levels in the blood, increasing the risk of side effects.
- CYP3A4 inducers: Conversely, medications like rifampin (antibiotic) and St. John’s Wort (herbal supplement) can speed up Viagra’s breakdown, potentially reducing its effectiveness.
Specific examples of interacting drugs include, but aren’t limited to:
- Ritonavir: A powerful HIV protease inhibitor.
- Ketoconazole: A commonly used antifungal medication.
- Erythromycin: A macrolide antibiotic.
- Terazosin: An alpha-blocker used to treat high blood pressure and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
- Nitroglycerin: Used to treat angina pectoris.
This is not an exhaustive list. Many other medications can interact with Viagra. Always provide your doctor with a complete list of all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting Viagra or any new medication.
Ignoring potential interactions can have serious health consequences. Open communication with your healthcare provider is crucial for safe and effective medication use.
Dangerous Combinations: Viagra and Nitrates
Never take Viagra (sildenafil) with nitrates. This combination can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness, fainting, heart attack, or stroke. Nitrates are found in many heart medications, including nitroglycerin, isosorbide mononitrate, and isosorbide dinitrate. These medications are often prescribed for angina (chest pain).
Understanding the Risk
Viagra and nitrates both relax blood vessels. When taken together, this effect is amplified, potentially causing a dangerously low blood pressure. This risk applies to all forms of nitrates, including those taken as pills, patches, or sprays. The interaction can occur even with small doses of either medication.
What to Do
If you are prescribed nitrates for heart conditions, discuss with your doctor *before* taking any medication for erectile dysfunction, including Viagra. Your physician can assess your overall health and suggest appropriate treatment options. If you experience chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness after taking Viagra, seek immediate medical attention. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Alternative Treatments
Many alternative treatments for erectile dysfunction exist. Your doctor can discuss these options with you, considering your medical history and other medications you may be taking. These alternatives might include other PDE5 inhibitors (like tadalafil or vardenafil), injection therapy, or vacuum erection devices. Open communication with your healthcare provider is key to safe and effective treatment.
Viagra and Blood Pressure Medications: Potential Risks and Precautions
Never take Viagra if you’re currently using nitrates for chest pain. This combination can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure, potentially leading to fainting or even a heart attack.
Understanding the Interaction
Viagra, or sildenafil, works by increasing blood flow. Many blood pressure medications also affect blood flow. This overlap can create unpredictable effects. The risk is particularly high with medications like:
- Alpha-blockers (e.g., terazosin, doxazosin): These relax blood vessels, similarly to Viagra, potentially causing excessive blood pressure reduction.
- Guanylate cyclase stimulators (e.g., riociguat): These drugs, like Viagra, increase blood flow, creating a synergistic and potentially dangerous effect.
Other blood pressure medications might also increase the risk of side effects when combined with Viagra. These effects can range from headaches and flushing to more serious issues.
Safe Practices
- Consult your doctor: Always discuss any medication changes, including starting Viagra, with your physician. They can assess your specific situation and medication interactions.
- Provide a complete medication list: Include all prescription, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements when speaking to your doctor or pharmacist.
- Start with a low dose: Your doctor may recommend a lower dose of Viagra to minimize potential side effects when taken with blood pressure medications.
- Monitor blood pressure: Regular blood pressure checks are crucial, especially when starting Viagra alongside other medications.
- Be aware of symptoms: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe dizziness, chest pain, or irregular heartbeat after taking Viagra.
Specific Blood Pressure Medication Considerations
Each blood pressure medication interacts differently with Viagra. Your doctor will personalize your treatment plan based on your specific drugs and health status.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and doesn’t replace professional medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before making any decisions about your medication.
Viagra and Antidepressants: Considerations for Concurrent Use
Consult your doctor before combining Viagra (sildenafil) with antidepressants. Many antidepressants, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), can interact with Viagra, potentially leading to a dangerous drop in blood pressure or other adverse effects.
Specific Antidepressant Interactions
SSRIs like sertraline (Zoloft), paroxetine (Paxil), fluoxetine (Prozac), and citalopram (Celexa) can increase Viagra’s effects, potentially causing prolonged erections (priapism) or dangerously low blood pressure. SNRIs such as venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta) present similar risks. Always disclose all medications you’re taking to your doctor and pharmacist.
Managing Potential Risks
Your physician might adjust your antidepressant dosage or suggest an alternative medication with fewer interaction risks. They may also recommend a lower Viagra dose to mitigate the chances of side effects. Regular monitoring of your blood pressure is crucial during concurrent use. Open communication with your healthcare provider is paramount for safe medication management.
Alternative Treatments
If you experience difficulties with erectile dysfunction and are taking antidepressants, discuss alternative treatments with your doctor. They might explore non-drug approaches like lifestyle modifications or recommend different erectile dysfunction medications that have fewer interactions with your antidepressants.
Viagra and Alpha-Blockers: Managing Potential Side Effects
Combining Viagra (sildenafil) with alpha-blockers can cause a significant drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness or fainting. Your doctor should carefully monitor your condition if you’re taking both medications.
Understanding the Interaction
Alpha-blockers relax blood vessels, lowering blood pressure. Viagra also has vasodilating effects. This combined effect can be pronounced, especially if you’re already on a high dose of either medication. The risk is greatest when starting either medication or adjusting dosages.
Minimizing Risks
Your physician will likely adjust your medication dosages gradually. Starting with the lowest effective dose of both Viagra and the alpha-blocker is standard practice. Regular blood pressure monitoring is critical, especially during the initial adjustment phase.
Managing Symptoms
If you experience dizziness or lightheadedness, sit or lie down immediately. Drink fluids to help alleviate the symptoms. Report any concerning symptoms to your doctor promptly.
Dosage Considerations
| Medication | Potential Interaction | Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Viagra (Sildenafil) | Significant blood pressure drop when combined with alpha-blockers. | Start with lowest effective dose; gradual dosage increases under medical supervision. |
| Alpha-blockers (e.g., Doxazosin, Terazosin) | Blood pressure lowering effect enhanced by Viagra. | Careful monitoring of blood pressure; dosage adjustments as needed. |
Seeking Medical Advice
Open communication with your doctor is paramount. Discuss all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. This helps them assess potential interactions and create a safe treatment plan. Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor if you have questions or concerns.
Alternative Treatments
If the combination proves problematic, your doctor may explore alternative treatments for erectile dysfunction or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), depending on your condition.
Viagra and Antifungal Medications: Important Interactions to Note
Certain antifungal medications can interact negatively with Viagra (sildenafil). This interaction primarily stems from how both drug types affect the body’s enzymes, specifically those involved in metabolizing medications.
Specifically, some azole antifungals, such as ketoconazole and itraconazole, inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for breaking down sildenafil. This inhibition leads to increased sildenafil levels in the bloodstream.
- Increased Side Effects: Higher sildenafil concentrations can amplify side effects, including headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. In rare instances, more serious side effects are possible.
- Elevated Blood Pressure: The combination can also potentially increase blood pressure, posing a risk for individuals with hypertension or cardiovascular conditions.
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Viagra or any other prescription drug.
- Consult your physician: Discuss your antifungal medication use with your doctor *before* beginning Viagra therapy. They can assess your individual risk and adjust dosages or recommend alternatives if necessary.
- Monitor for side effects: Pay close attention to any unusual symptoms after starting Viagra, especially if you’re also taking an antifungal medication. Report any concerns to your healthcare provider.
- Consider alternative treatments: If a specific antifungal is unavoidable, your doctor might explore alternative erectile dysfunction treatments to minimize risks.
This information is for educational purposes and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Seeking Professional Guidance: Importance of Doctor Consultation
Always consult your doctor before starting any medication, including Viagra or other prescription drugs. This ensures the medication is safe for you, considering your overall health and any pre-existing conditions. Your doctor will review your medical history, perform a physical examination, and potentially order blood tests to assess your suitability for Viagra or alternative treatments.
Understanding Potential Interactions
Many medications interact with Viagra. Your physician can identify potential drug interactions and adjust your medication plan accordingly, minimizing the risk of adverse effects. For example, nitrates, often prescribed for heart conditions, can cause dangerously low blood pressure when combined with Viagra. Proper consultation prevents such risks.
Personalized Treatment Plan
Viagra isn’t suitable for everyone. Your doctor can determine if Viagra is the right treatment for you, or if alternative therapies are more appropriate. They may discuss lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, to improve erectile dysfunction. They can also offer guidance on managing underlying health issues contributing to the condition. This tailored approach improves outcomes and minimizes unwanted side effects.
Monitoring Your Progress
Regular check-ups allow your doctor to monitor your response to treatment and adjust your medication or treatment plan if needed. This ongoing care is particularly important for managing potential side effects and ensuring optimal results. Open communication with your physician throughout the process facilitates better health management.