Begin with your doctor’s recommendations. They’ll personalize your dosage based on your health and medical history. The typical starting dose is 50mg, taken as needed, about an hour before sexual activity.
Don’t exceed 100mg per day. Higher doses don’t necessarily enhance effectiveness and may increase the risk of side effects. Remember, consistent adherence to your prescribed dosage is crucial.
Absorption is affected by food. Taking Viagra with a high-fat meal may delay its onset. For optimal results, take it on an empty stomach or with a light meal. Frequency should align with your doctor’s advice; it’s not designed for daily use unless specifically instructed.
Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. These are usually mild and temporary. Severe side effects, such as chest pain or prolonged erection, require immediate medical attention. Consult your physician about any concerns.
Always store Viagra at room temperature, away from moisture and direct sunlight. Keep it out of children’s reach. Discard any expired medication appropriately. Regular check-ups with your doctor will help monitor your progress and address any questions.
- Viagra Dosage and Administration: A Detailed Guide
- Recommended Starting Dose of Viagra
- Adjusting Viagra Dosage Based on Response and Tolerance
- Insufficient Response
- Side Effects
- Individual Variation
- Frequency of Dosage
- Viagra Dosage for Specific Medical Conditions
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Dosage Adjustments Based on Liver and Kidney Function
- Interaction with other Medications
- Taking Viagra with Food and Alcohol
- Alcohol and Viagra
- Frequency of Viagra Use: How Often Can You Take It?
- Missed Dose of Viagra: What to Do
- Potential Side Effects and Interactions with Other Medications
- Overdosing on Viagra: Symptoms and Treatment
- Managing a Viagra Overdose
- Prevention
Viagra Dosage and Administration: A Detailed Guide
The recommended starting dose of Viagra is 50 mg taken orally, approximately one hour before sexual activity.
Your doctor may adjust this based on your individual needs and response. Common dosage adjustments include:
- Increased dosage: If 50mg is ineffective, your doctor might increase it to 100mg. This is the maximum recommended dose.
- Decreased dosage: If you experience side effects, your doctor may reduce the dosage to 25mg.
Dosage frequency should not exceed once daily.
Here’s what to remember about administration:
- Take Viagra as directed by your physician. Do not alter your dosage without consulting them.
- Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not crush or chew the tablet.
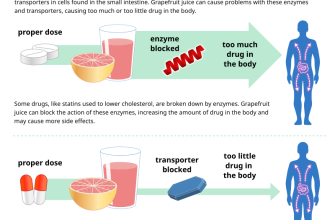
- Viagra’s effects can be influenced by food. A high-fat meal may delay the onset of action. Consider this when planning your timing.
- Alcohol consumption may increase the risk of side effects. Moderate your alcohol intake while taking Viagra.
- Certain medical conditions and medications can interact with Viagra. Be sure to disclose all health issues and medications you are currently taking to your doctor.
If you experience any adverse effects, contact your doctor immediately. Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. Severe side effects are rare but require immediate medical attention.
This guide provides general information. Always follow your doctor’s specific instructions regarding Viagra dosage and administration.
Recommended Starting Dose of Viagra
The usual starting dose of Viagra is 50 mg taken as needed, approximately one hour before sexual activity.
However, your doctor might recommend a lower dose (25 mg) depending on your individual health conditions and response to the medication. A higher dose (100 mg) may be considered if the 50 mg dose is not effective, but this should only be done under strict medical supervision.
Never exceed the recommended dose without consulting your physician. Dosage adjustments should always be made in consultation with your doctor based on your individual needs and tolerance.
Remember to take Viagra only as directed by your healthcare provider. Follow their instructions carefully for safe and effective use.
Adjusting Viagra Dosage Based on Response and Tolerance
If you experience satisfactory results with 50 mg, maintain that dosage. However, if you don’t achieve the desired effect, your doctor might increase it to 100 mg. This is the maximum recommended dose.
Insufficient Response
If 100 mg provides inadequate improvement, consider discussing alternative treatment options with your physician. They can help explore different approaches to managing erectile dysfunction. Don’t attempt to exceed the recommended dosage without medical advice.
Side Effects
Side effects, such as headaches, flushing, or nasal congestion, are common. If these are mild and manageable, you may continue treatment. However, significant side effects necessitate a dosage reduction or a switch to a different medication. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience severe side effects. A lower dose of 25 mg might be more suitable if needed. Always follow your doctor’s instructions.
Individual Variation
Remember, Viagra’s impact varies from person to person. Factors like age, overall health, and other medications affect the response. Open communication with your doctor is critical for personalized dosage adjustment and optimal management of your condition. Regular checkups allow for ongoing assessment and necessary modifications to your treatment plan.
Frequency of Dosage
Do not take Viagra more than once a day. The medication’s effect lasts for several hours. Taking more won’t enhance results and may increase the risk of side effects.
Viagra Dosage for Specific Medical Conditions
Dosage adjustments are often necessary depending on individual health factors. Always consult your physician for personalized guidance.
Pulmonary Hypertension
For pulmonary hypertension, Viagra (sildenafil) is prescribed at a lower dose than for erectile dysfunction. Typical starting dosages range from 20mg to 40mg three times daily. Your doctor will carefully monitor your response and adjust the dosage accordingly. Close monitoring of blood pressure is crucial.
Erectile Dysfunction
The recommended starting dose for erectile dysfunction is typically 50mg, taken as needed, about one hour before sexual activity. Your doctor may adjust this to 25mg or 100mg based on your response and tolerance. Do not exceed 100mg per dose.
Dosage Adjustments Based on Liver and Kidney Function
| Condition | Dosage Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Mild hepatic impairment | Start with 25mg |
| Moderate hepatic impairment | Start with 25mg; maximum dose 50mg |
| Severe hepatic impairment | Not recommended |
| Severe renal impairment | Start with 25mg; may need dosage adjustment. |
Interaction with other Medications
Viagra can interact with certain medications, potentially affecting its efficacy or causing side effects. Always inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements, you are currently taking. They will assess potential interactions and adjust the dosage accordingly.
Taking Viagra with Food and Alcohol
Avoid taking Viagra with a high-fat meal. Fatty foods significantly delay absorption, potentially reducing effectiveness and prolonging onset. A light meal or snack is preferable.
Alcohol and Viagra
Combining Viagra and alcohol can lower blood pressure, potentially leading to dizziness or fainting. Moderate alcohol consumption might be tolerated, but excessive drinking significantly increases the risk of side effects. It’s best to avoid alcohol entirely when taking Viagra.
Always consult your doctor before mixing Viagra with any other medication or substance, including alcohol. They can provide personalized advice based on your health and medical history. Your doctor can help you determine a safe and effective approach.
Frequency of Viagra Use: How Often Can You Take It?
The recommended maximum dose of Viagra is one 50mg tablet per day. This is a general guideline; your doctor may adjust this based on your individual needs and health status.
Taking Viagra more frequently than prescribed can increase the risk of side effects. These side effects can range from mild, such as headaches or flushing, to more serious, such as vision changes or hearing loss. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully.
The time between doses should be at least 24 hours. This allows your body to fully metabolize the medication, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions. Don’t exceed the recommended dosage even if you don’t experience the desired effect.
If you experience any concerning side effects, contact your doctor immediately. They can assess your situation and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
Remember, Viagra is a prescription medication. Self-medicating or altering the prescribed dosage can be dangerous. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication, including Viagra, and discuss any concerns you may have.
Missed Dose of Viagra: What to Do
Don’t take a double dose to make up for a missed one. This can increase your risk of side effects.
Instead, simply skip the missed dose and take your next dose as scheduled.
- If you’re unsure when to take your next dose, check your prescription label or contact your doctor or pharmacist for guidance. They can clarify your dosing schedule.
- Regularly scheduled dosing is key. Consistency helps maximize effectiveness and minimizes potential problems.
- Never exceed the recommended dose. Your doctor prescribed a specific amount for a reason. Adjusting this independently could be harmful.
If you frequently miss doses, discuss this with your doctor. They may adjust your treatment plan or explore alternative options to ensure you’re receiving the appropriate medication regimen.
Remember to always store Viagra according to the instructions on the label to maintain its potency.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions with Other Medications
Viagra, like many medications, can cause side effects. Common ones include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and upset stomach. Less frequent, but more serious, side effects include vision changes (blurred vision, blue-tint vision), hearing loss, and prolonged erection (priapism). Seek immediate medical attention if you experience a prolonged erection lasting more than four hours.
Important Note: This list isn’t exhaustive. Consult your doctor for a complete list and to discuss any concerns.
Viagra interacts with certain medications. Nitrates, often used to treat chest pain (angina), are a serious concern. Combining them with Viagra can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure. Similarly, alpha-blockers, commonly prescribed for high blood pressure or enlarged prostate, can also increase the risk of low blood pressure when taken with Viagra.
Other medications that may interact include certain antifungal medications, HIV protease inhibitors, and some antibiotics. Always inform your doctor and pharmacist about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you are taking before starting Viagra. This helps avoid potentially hazardous interactions.
If you experience any unexpected side effects, contact your doctor or other healthcare professional immediately. They can provide personalized advice and manage any adverse reactions.
Overdosing on Viagra: Symptoms and Treatment
Seek immediate medical attention if you suspect a Viagra overdose. Symptoms can include chest pain, irregular heartbeat, vision changes (blurred vision, sudden vision loss), prolonged erection (priapism), and hearing loss. Severe cases may involve seizures or a heart attack.
Managing a Viagra Overdose
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and supporting vital functions. This may include administering oxygen, intravenous fluids, and medications to lower blood pressure or control heart rhythm. For priapism, specific treatments to relieve the prolonged erection are necessary. A healthcare professional will determine the best course of action based on your individual symptoms and health history.
Prevention
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage and instructions. Never take more Viagra than recommended, and avoid combining it with other medications or recreational drugs without consulting your physician. Open communication with your doctor is vital for safe and effective medication management.