No, current research doesn’t show a direct causal link between Viagra (sildenafil) and hair loss. While some anecdotal evidence exists, major studies haven’t established a connection. This doesn’t mean individual experiences are invalid; individual reactions to medication vary.
However, underlying health conditions can impact both erectile dysfunction and hair loss. For instance, hormonal imbalances or conditions like diabetes can affect both. If you’re experiencing both, address the root cause with your doctor–treating the underlying condition might improve both issues.
Remember, Viagra’s primary function is to improve blood flow. While increased blood flow *can* sometimes benefit hair growth, there’s no guarantee, and this effect isn’t the drug’s intended purpose. Side effects are possible, and a consultation with your healthcare provider before starting any medication is crucial. Discuss your concerns about potential side effects, including hair loss, to ensure the medication is safe for you.
Key takeaway: While Viagra itself is unlikely to cause hair loss, underlying health concerns should be investigated if you’re experiencing both issues. Always consult your doctor before starting any new medication.
- Does Viagra Cause Hair Loss?
- Underlying Health Conditions and Hair Loss
- Other Factors Affecting Hair Loss
- Recommendations
- Viagra and Hair Growth
- Viagra’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Hair Loss Links
- PDE5 and Hair Growth
- Viagra and Hair Loss: The Current Evidence
- Studies Examining Viagra and Hair Loss: What the Research Says
- Other Medications That Can Cause Hair Loss: Comparing Viagra to Alternatives
- Hair Loss and Other Medications
- Lifestyle Factors Affecting Hair Loss: Separating Viagra’s Role
- Nutrition and Hair Health
- Addressing Underlying Medical Conditions
- Managing Hair Loss: Strategies and When to Seek Professional Help
Does Viagra Cause Hair Loss?
No, Viagra (sildenafil) itself doesn’t directly cause hair loss. However, certain underlying health conditions that may lead to erectile dysfunction, for which Viagra is prescribed, can also contribute to hair loss.
Underlying Health Conditions and Hair Loss
Conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease are sometimes associated with both erectile dysfunction and hair loss. Treatment for these conditions, not Viagra itself, might indirectly influence hair growth. For example, some medications used to manage these conditions can have hair loss as a side effect.
- High blood pressure: Some blood pressure medications can impact hair follicles.
- Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can negatively affect hair growth.
- Heart disease: Certain heart conditions and their treatments can sometimes contribute to hair loss.
Other Factors Affecting Hair Loss
Stress, hormonal changes (particularly in men), age, and genetics all play significant roles in hair loss. It’s crucial to distinguish between hair loss caused by these factors and any potential connection to Viagra treatment.
Recommendations
- Consult a doctor: If you’re experiencing hair loss, discuss it with your doctor. They can help identify the cause and suggest appropriate treatment options.
- Review medications: A complete medication review can help identify if a prescribed drug might be contributing to hair loss.
- Address underlying conditions: Managing underlying health issues effectively can often positively impact hair growth.
Viagra and Hair Growth
Currently, there’s no evidence suggesting Viagra promotes or inhibits hair growth. Focusing on addressing any underlying medical issues is key to managing both erectile dysfunction and potential hair loss.
Viagra’s Mechanism of Action and Potential Hair Loss Links
Viagra, or sildenafil, primarily works by inhibiting an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). This increases blood flow to the penis, facilitating erections. However, PDE5 is also found in other parts of the body, including hair follicles.
PDE5 and Hair Growth
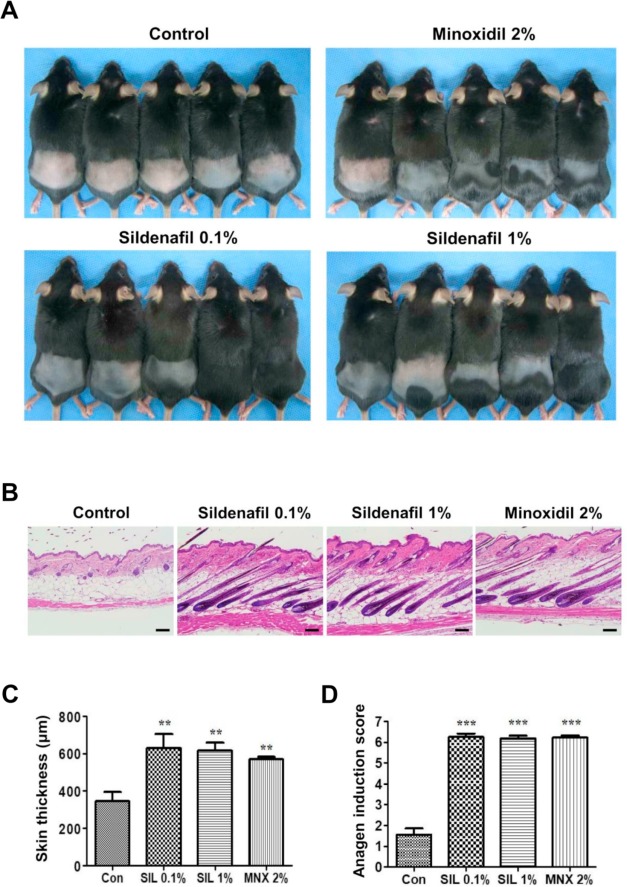
Some research suggests a potential link between PDE5 inhibition and hair growth. Increased blood flow, a direct consequence of Viagra’s action, could theoretically improve nutrient delivery to hair follicles. This might stimulate hair growth, or at least slow down hair loss. However, this is not definitively established, and the impact, if any, is likely minimal.
Viagra and Hair Loss: The Current Evidence
Currently, there’s no strong clinical evidence directly linking Viagra use to hair loss. While some anecdotal reports exist, these are not sufficient to confirm a causal relationship. Further studies are needed to explore this potential side effect thoroughly. Any observed hair loss in Viagra users likely stems from unrelated factors, such as underlying medical conditions or other medications.
Consult your doctor to discuss any concerns about hair loss, regardless of your medication use. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend suitable treatment options.
Studies Examining Viagra and Hair Loss: What the Research Says
Direct links between Viagra (sildenafil) and hair loss remain inconclusive. While some studies suggest a potential correlation, definitive causal evidence is lacking.
A 2018 study published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine explored the relationship between phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors, including Viagra, and hair loss. This observational study showed a possible association, but it didn’t prove causation. Further research is needed to clarify this potential link.
Another area of investigation focuses on the effects of sildenafil on hormones, particularly testosterone levels. Fluctuations in testosterone can impact hair growth. However, current research does not consistently demonstrate a significant impact of Viagra on testosterone sufficient to explain hair loss.
It’s crucial to remember that many factors contribute to hair loss, including genetics, age, stress, and underlying medical conditions. Viagra might be a contributing factor in some individuals, but its role is likely small compared to these other elements.
| Study | Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 Journal of Sexual Medicine | Possible association between PDE5 inhibitors and hair loss observed. | Observational study; correlation does not equal causation. |
| Various hormone studies | Inconclusive evidence regarding significant impact of Viagra on testosterone levels. | Varied methodologies; need for larger, more controlled studies. |
If you experience hair loss and take Viagra, discuss your concerns with your doctor. They can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate management strategies.
Other Medications That Can Cause Hair Loss: Comparing Viagra to Alternatives
While Viagra (sildenafil) isn’t directly linked to significant hair loss, certain other medications used to treat erectile dysfunction or related conditions can contribute to hair thinning. For example, some antihypertensive medications, often prescribed alongside Viagra for patients with hypertension and ED, can cause hair loss as a side effect. Beta-blockers, a common class of antihypertensives, are known to sometimes lead to this issue. Always discuss potential side effects with your doctor before starting any new medication.
Hair Loss and Other Medications
Beyond erectile dysfunction treatments, several other drug classes frequently cause hair thinning. Certain antidepressants, particularly those in the tricyclic class, can trigger hair loss. Similarly, some anticoagulants, like warfarin, have been associated with this side effect in certain individuals. Steroids, while powerful, can also impact hair growth, causing significant thinning during prolonged use. This side effect is dose-related and often reversible upon discontinuation. Finally, anti-cancer medications, due to their mechanism of action, can unfortunately cause hair loss as a common side effect. Your doctor can help you weigh the benefits against the potential side effects of any medicine.
Remember to openly communicate any concerns about hair loss with your healthcare provider. They can help determine if the medication is the cause, and suggest management strategies or alternative treatments if necessary.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Hair Loss: Separating Viagra’s Role
Focus on managing stress. High stress levels correlate with increased hair shedding. Consider incorporating stress-reduction techniques like regular exercise, yoga, or meditation into your daily routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly.
Nutrition and Hair Health
A balanced diet rich in protein, iron, and zinc is crucial for healthy hair growth. Protein forms the building blocks of hair. Iron deficiency is a common cause of hair loss, while zinc supports hair follicle function. Include lean meats, beans, leafy greens, and nuts in your diet. Consult a doctor or registered dietitian to address any nutritional deficiencies.
Smoking significantly impacts hair health. Nicotine restricts blood flow to the scalp, hindering nutrient delivery to hair follicles. Quitting smoking is one of the most impactful steps you can take to improve your overall health, including hair health. Seek support from cessation programs if needed.
While Viagra’s potential link to hair loss warrants discussion with your doctor, lifestyle modifications often address the majority of hair loss concerns. Proper nutrition, stress management, and avoiding smoking are critical factors to consider.
Addressing Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can cause hair loss. These include thyroid problems, autoimmune disorders, and hormonal imbalances. If you experience unexplained hair loss, consult your physician for a thorough evaluation and appropriate medical management. Early diagnosis and treatment of underlying conditions are crucial for effective hair loss management.
Managing Hair Loss: Strategies and When to Seek Professional Help
Maintain a healthy diet rich in protein, iron, and zinc. These nutrients support hair growth.
Reduce stress through techniques like yoga or meditation. Stress significantly impacts hair health.
Gently massage your scalp to improve blood circulation, potentially stimulating hair follicles.
Consider using minoxidil or other FDA-approved hair loss treatments. Always follow product instructions carefully.
Explore low-level laser therapy (LLLT) options. Studies suggest potential benefits for hair regrowth.
Protect your hair from harsh sun exposure by wearing a hat or using UV-protective products.
Avoid tight hairstyles that pull on the hair and can lead to traction alopecia.
Consult a dermatologist or trichologist if hair loss is rapid, patchy, or accompanied by other symptoms. They can diagnose the cause and recommend tailored treatment.
Genetic predisposition plays a large role. Understanding your family history helps manage expectations.
Be patient. Hair growth treatments often take several months to show results.
Medical conditions like thyroid problems or autoimmune diseases can cause hair loss. Addressing underlying health issues is crucial.