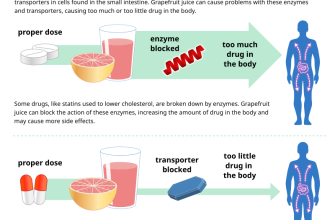
Need to know how Viagra interacts with other medications? Start by checking for potential drug interactions. Consult your doctor or pharmacist; they’ll provide personalized guidance based on your specific medications and health conditions. This is crucial to avoid unexpected side effects.
Certain medications can significantly alter Viagra’s effectiveness or increase the risk of adverse reactions. For instance, nitrates, commonly used to treat chest pain (angina), interact dangerously with Viagra, potentially causing a drastic drop in blood pressure. Similarly, some antibiotics, antifungals, and medications for high blood pressure can influence Viagra’s performance.
Always disclose all medications you are currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, to your healthcare provider before starting Viagra. This includes herbal remedies and recreational drugs. Open communication is key to ensuring your safety and achieving the desired therapeutic outcome. Don’t hesitate to ask your doctor any questions you might have about potential risks or interactions.
Remember: This information isn’t a substitute for professional medical advice. Seek personalized guidance from a qualified healthcare professional to manage your medications safely and effectively. Your health and well-being are paramount.
- Drugs with Viagra: Understanding Interactions and Risks
- Viagra and Nitrates: A Dangerous Combination
- Viagra and Alpha-Blockers: Potential for Low Blood Pressure
- Viagra and Antifungal Medications: Impact on Efficacy
- Viagra and HIV Medications: Possible Interactions
- Ritonavir and other protease inhibitors
- Other HIV medications
- Specific Recommendations
- Possible Side Effects to Watch For
- Alternative Treatments
- Viagra and Heart Medications: Considerations for Patients with Cardiovascular Issues
- Viagra and Blood Thinners: Increased Risk of Bleeding
- Understanding the Interaction
- What You Should Do
- Monitoring for Bleeding
- Alternative Treatments
- Viagra and Alcohol: Enhancing Side Effects
- Viagra and Other Erectile Dysfunction Drugs: Avoiding Overdosing and Interactions
- Understanding Potential Interactions
- Knowing the Side Effects
- Safe Medication Management
- Seeking Professional Guidance
- Alcohol and Viagra
Drugs with Viagra: Understanding Interactions and Risks
Always talk to your doctor before mixing Viagra (sildenafil) with other medications. Certain drugs can significantly affect how Viagra works and increase the risk of side effects.
Here’s what you need to know:
- Nitrates: Combining Viagra with nitrates (used to treat chest pain) can cause a dangerous drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness, fainting, or even a heart attack. This combination is strictly prohibited.
- Alpha-blockers: These medications, often prescribed for high blood pressure or enlarged prostate, can also lower blood pressure when taken with Viagra, increasing the risk of hypotension. Your doctor may adjust your dosages.
- Blood Thinners: While not a direct contraindication, combining Viagra with blood thinners (like warfarin) may increase the risk of bleeding. Close monitoring is advisable.
- Certain Antifungal Medications: Some antifungals can interfere with Viagra’s metabolism, potentially increasing its concentration in your blood and raising the risk of side effects.
- HIV Protease Inhibitors: These drugs can also increase Viagra’s levels in your blood, prompting similar concerns regarding side effects.
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: This group of drugs (including some antibiotics and antifungals) inhibit the enzyme that metabolizes Viagra. This can lead to higher blood levels of Viagra and heightened risk of side effects.
Specific interactions and their potential severity vary depending on the dose and individual health conditions.
- Always provide a complete medication list to your doctor, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies.
- Never self-medicate. Discuss any concerns about medication interactions with your physician before starting or altering any treatment plan.
- Be aware of potential side effects. These can include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, visual disturbances, and muscle aches. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe side effects.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Consult your doctor for personalized guidance regarding Viagra and its interaction with other medications.
Viagra and Nitrates: A Dangerous Combination
Never take Viagra (sildenafil) if you’re using nitrates. This combination can cause a significant drop in blood pressure, leading to serious health risks.
Nitrates are found in many medications, including:
- Nitroglycerin (used for angina)
- Isosorbide dinitrate (also for angina)
- Isosorbide mononitrate (for angina and heart failure)
These medications work by relaxing blood vessels. Viagra does the same. The combined effect can be dangerously low blood pressure, potentially resulting in:
- Fainting
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Even death
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, before starting Viagra or any other medication for erectile dysfunction.
If you experience chest pain, dizziness, or lightheadedness after taking Viagra, seek immediate medical attention. This could indicate dangerously low blood pressure.
This information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult your doctor or pharmacist for personalized guidance.
- Check your medications carefully. Look for the active ingredients listed above.
- Talk to your doctor about alternative treatments for erectile dysfunction if you are on nitrate medication.
- Understand the risks. Be aware of potential side effects and seek help immediately if needed.
Viagra and Alpha-Blockers: Potential for Low Blood Pressure
Combining Viagra (sildenafil) and alpha-blockers can significantly lower blood pressure. This is because both medications relax blood vessels. Alpha-blockers, prescribed for conditions like high blood pressure and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), reduce vascular resistance. Viagra further enhances this effect, potentially leading to dangerously low blood pressure, especially upon initial use.
Symptoms of dangerously low blood pressure include dizziness, fainting, and lightheadedness. If you experience these, seek immediate medical attention.
Your doctor should carefully monitor your blood pressure if you’re taking both medications. They might adjust dosages or recommend alternative treatments.
| Medication Combination | Potential Risk | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Viagra & Alpha-blockers (e.g., tamsulosin, terazosin) | Orthostatic hypotension (sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing) | Start with low doses of both medications; monitor blood pressure regularly; avoid sudden changes in posture; stay hydrated. |
Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. Open communication is key to managing potential drug interactions safely. This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.
Viagra and Antifungal Medications: Impact on Efficacy
Concurrent use of Viagra (sildenafil) and certain antifungal medications can affect Viagra’s effectiveness. Azole antifungals, such as ketoconazole and itraconazole, inhibit the liver enzyme CYP3A4, which is responsible for metabolizing sildenafil. This inhibition leads to increased sildenafil blood levels, potentially increasing the risk of side effects like hypotension and prolonged erection (priapism).
Conversely, some antifungals, like fluconazole, have a weaker effect on CYP3A4. Their interaction with sildenafil is generally less significant, but still warrants caution. Always inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements.
Specific Recommendations: If you’re prescribed both Viagra and an azole antifungal, your doctor might adjust the Viagra dosage to mitigate risks. They may also suggest an alternative antifungal medication with less CYP3A4 inhibition. Close monitoring of blood pressure is advisable during concurrent treatment.
Remember: This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance based on your individual health status and medical history. Never alter your medication regimen without first consulting your physician.
Viagra and HIV Medications: Possible Interactions
Always discuss all medications you take with your doctor before starting Viagra (sildenafil). Several HIV medications can interact with Viagra, potentially causing dangerous side effects.
Ritonavir and other protease inhibitors
Ritonavir, indinavir, and other protease inhibitors significantly increase Viagra’s levels in your blood. This heightened concentration can lead to a greater risk of side effects like low blood pressure, fainting, and vision problems. Your doctor may need to adjust your Viagra dosage or consider alternative treatments.
Other HIV medications
- Some non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), like efavirenz, can decrease Viagra’s effectiveness.
- Interactions with other HIV medications are less common, but are still possible. Always provide your doctor with a complete list of all your medications.
Specific Recommendations
- Be completely transparent with your doctor about all the drugs you’re taking, including over-the-counter medications and supplements.
- Never adjust your medication dosage without consulting your doctor.
- Regularly monitor your blood pressure and report any unusual symptoms promptly to your physician.
- Understand that the potential for interaction depends on factors like dosage and individual metabolism. Your physician will assess your specific circumstances.
Possible Side Effects to Watch For
Increased risk of side effects from Viagra when taken with certain HIV medications might include: headache, flushing, nasal congestion, visual disturbances, and muscle pain. Severe side effects, though less common, warrant immediate medical attention.
Alternative Treatments
If interactions are a concern, your doctor might recommend alternative erectile dysfunction treatments. These could include other PDE5 inhibitors, or therapies like vacuum erection devices or injections.
Viagra and Heart Medications: Considerations for Patients with Cardiovascular Issues
Consult your doctor before using Viagra if you have heart problems. Viagra, or sildenafil, lowers blood pressure, which can be dangerous for those with certain heart conditions. This interaction is particularly relevant if you’re taking nitrates, often prescribed for angina (chest pain). The combined effect can cause a significant drop in blood pressure, potentially leading to dizziness, fainting, or even a heart attack.
Alpha-blockers, used to treat high blood pressure and enlarged prostate, can also interact negatively with Viagra. This combination may further reduce blood pressure, increasing the risk of adverse effects. Your doctor will need to assess your overall cardiovascular health and medication regimen before recommending Viagra.
Certain heart medications can affect how your body processes Viagra. This can lead to either increased side effects or reduced effectiveness. Open communication with your cardiologist and your prescribing doctor is critical to avoid unexpected interactions and ensure your safety. They will carefully weigh the risks and benefits based on your individual health profile.
Regular monitoring of your blood pressure is recommended if you use Viagra while taking heart medications. This helps detect potential problems early and allows for timely adjustments to your treatment plan. Don’t hesitate to contact your doctor immediately if you experience any unusual symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or irregular heartbeat.
Remember that this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always discuss your medication history with your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment, including Viagra.
Viagra and Blood Thinners: Increased Risk of Bleeding
Combining Viagra (sildenafil) with blood thinners increases your risk of bleeding. This is because Viagra can also lower blood pressure and affect blood clotting. The interaction isn’t always severe, but it warrants careful consideration.
Understanding the Interaction
Blood thinners, such as warfarin (Coumadin) or aspirin, reduce your blood’s ability to clot. Viagra, by relaxing blood vessels, further enhances this effect. This combination can lead to prolonged bleeding, even from minor injuries. Bruising may be more common, and more serious bleeding events, though uncommon, are possible.
What You Should Do
Open communication with your doctor is key. Before starting Viagra, especially if you’re already on blood thinners, discuss the potential risks and benefits. Your doctor will assess your overall health and determine if Viagra is safe for you. They may suggest alternative treatments or adjust your blood thinner dosage.
Monitoring for Bleeding
Pay close attention to your body. Report any unusual bleeding, such as nosebleeds, easy bruising, or bleeding gums, to your doctor immediately. Regular blood tests may be necessary to monitor your clotting factors while taking both medications.
Alternative Treatments
If the risk of bleeding is too high, your doctor might suggest alternative treatments for erectile dysfunction. Several options exist, and finding the right one depends on your individual circumstances.
Viagra and Alcohol: Enhancing Side Effects
Mixing Viagra (sildenafil) and alcohol can amplify side effects. Specifically, combining them increases the risk of experiencing headaches, flushing, and low blood pressure.
Low blood pressure, a common side effect intensified by alcohol, can lead to dizziness or fainting. This risk is especially pronounced with larger doses of either substance.
The effect on blood pressure might also influence your heart. While generally safe for healthy individuals, combining Viagra and alcohol increases cardiac strain, potentially problematic for those with pre-existing heart conditions.
Gastrointestinal issues, such as nausea and indigestion, are also more likely with this combination. Alcohol itself can irritate the stomach lining, and Viagra can have a similar effect, making the combination potentially uncomfortable.
Remember, individual reactions vary. Consult your doctor before mixing alcohol and Viagra, especially if you have underlying health problems. They can help assess your risk and provide personalized advice.
Viagra and Other Erectile Dysfunction Drugs: Avoiding Overdosing and Interactions
Always follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage. Never exceed the recommended dose of Viagra or any other erectile dysfunction medication. Taking more than prescribed won’t enhance the effect and can increase the risk of side effects.
Understanding Potential Interactions
Certain medications can interact dangerously with Viagra and similar drugs. These include nitrates (used to treat angina), some blood pressure medications, and certain antifungals. Discuss all your current medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, with your doctor before starting erectile dysfunction treatment. This ensures safe and appropriate medication combinations.
Knowing the Side Effects
Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. More serious, though rare, side effects include prolonged erection (priapism) and sudden vision or hearing loss. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these.
Safe Medication Management
| Medication Type | Potential Interaction with Viagra | Action to Take |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrates | Severe drop in blood pressure, potentially life-threatening | Do not take Viagra if you use nitrates. |
| Alpha-blockers | Increased risk of low blood pressure | Your doctor may adjust dosages or prescribe alternative treatments. |
| CYP3A4 Inhibitors | Increased Viagra levels in the blood, potentially leading to increased side effects | Your doctor may adjust the Viagra dosage. |
Seeking Professional Guidance
If you have questions about dosage, potential interactions, or side effects, contact your doctor or pharmacist immediately. They can provide personalized advice based on your health history and medication profile. Open communication is key to safe and effective treatment.
Alcohol and Viagra
Avoid excessive alcohol consumption while taking Viagra. Alcohol can amplify side effects and potentially interact negatively with the medication.