Start with your doctor: Always consult a physician before using Viagra or any medication for erectile dysfunction. A proper diagnosis is crucial to ensure the medication is safe and appropriate for your individual health profile. Your doctor will assess your medical history and current health conditions to determine the correct dosage and discuss potential side effects.
Recommended Starting Dose: The typical starting dose of Viagra is 50mg. This dose is often effective for many men. However, your doctor might prescribe a lower dose (25mg) depending on your health status or adjust it to 100mg if needed. Never exceed the recommended dose without explicit instruction from your physician.
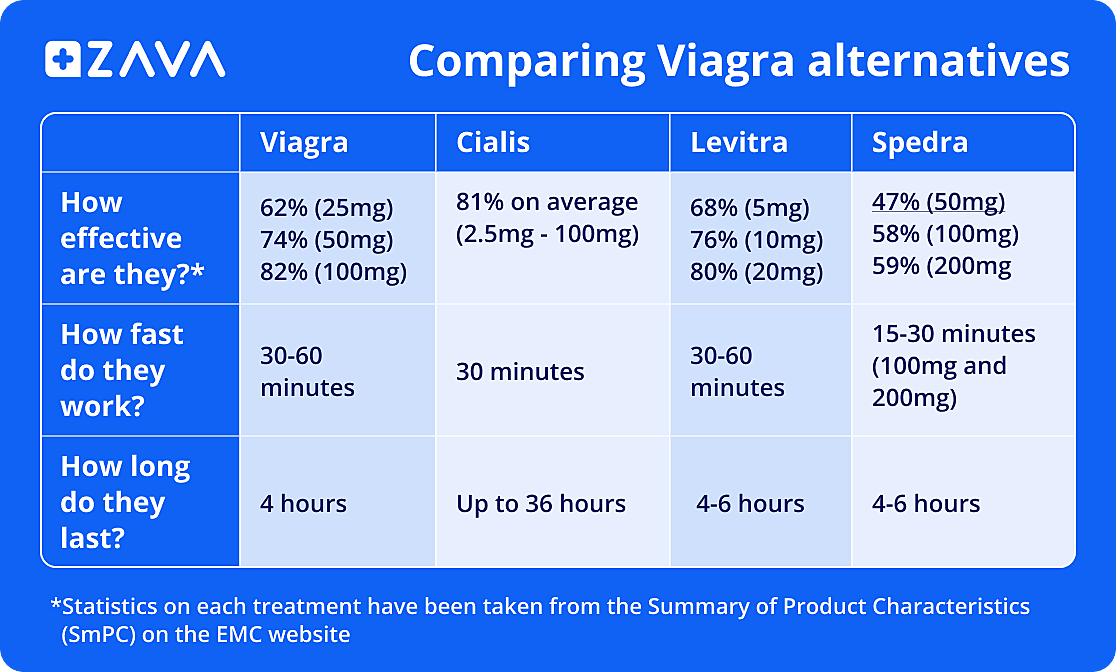
Dosage Frequency: Viagra is typically taken as needed, about 30-60 minutes before sexual activity. It’s important to understand that taking Viagra more than once a day is generally not advised. Discuss the appropriate frequency with your doctor; they will tailor the instructions to your specific needs.
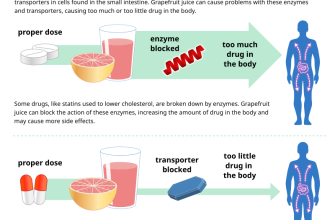
Important Considerations: Certain medical conditions, such as heart problems or low blood pressure, may interact negatively with Viagra. Openly discuss all your medications and health issues with your doctor to ensure safe usage. Grapefruit juice can also affect how your body processes Viagra; avoid it while taking this medication.
Side Effects: Common side effects include headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and upset stomach. Rarely, more serious side effects can occur. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience sudden vision loss, prolonged erection (priapism), or chest pain.
- Viagra Usage and Dosage
- Maximum Dosage and Frequency
- Factors Affecting Dosage
- Missed Dose
- Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
- Nitric Oxide’s Role
- Important Considerations
- Recommended Dosage and Administration
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions
- Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
- Nitrates and Viagra
- Alpha-Blockers
- Blood Thinners
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors
- Alcohol
- Grapefruit Juice
- Recreational Drugs
- Other Medications
Viagra Usage and Dosage
Always follow your doctor’s instructions. The typical starting dose is 50mg, taken as needed, about an hour before sexual activity. This dose may be increased to 100mg or decreased to 25mg, depending on your response and any side effects.
Maximum Dosage and Frequency
The maximum recommended dose is 100mg per day. Do not take more than one tablet in a 24-hour period. Consistent use exceeding this amount is unsafe and increases the risk of adverse reactions.
Factors Affecting Dosage
Your age, overall health, and other medications you’re taking significantly influence the appropriate Viagra dosage. Liver or kidney problems can require a lower dose. Interaction with other medications, especially nitrates, is dangerous and strictly prohibited. Consult your physician before using Viagra if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Missed Dose
Viagra is taken as needed, not on a regular schedule. If you miss a dose, simply take it as soon as you remember, but only if you plan on engaging in sexual activity. Do not double the dose to make up for a missed one.
Understanding Viagra’s Mechanism of Action
Viagra, or sildenafil, primarily works by inhibiting an enzyme called phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5). PDE5 breaks down cyclic GMP, a molecule crucial for achieving and maintaining an erection. By blocking PDE5, Viagra allows cyclic GMP levels to rise, leading to increased blood flow into the penis and facilitating an erection.
Nitric Oxide’s Role
The process begins with sexual stimulation, triggering the release of nitric oxide (NO). NO activates an enzyme called guanylate cyclase, which then produces cyclic GMP. This increased cyclic GMP relaxes the smooth muscles in the blood vessels of the penis, allowing for greater blood flow. Viagra enhances this effect by preventing the breakdown of cyclic GMP, prolonging the relaxation and facilitating a stronger erection.
Important Considerations
It’s important to remember that Viagra only works in the presence of sexual stimulation. It doesn’t directly cause an erection; it enhances the body’s natural response to sexual stimulation. The drug’s effects vary from person to person, and factors like age, overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions can influence its efficacy.
Recommended Dosage and Administration
The typical starting dose of Viagra is 50 mg, taken as needed, about one hour before sexual activity. However, your doctor may prescribe a lower dose (25 mg) or a higher dose (100 mg), depending on your individual needs and response to the medication.
Take Viagra only as directed by your physician. Do not exceed the recommended dose. The maximum recommended dose is 100 mg in a 24-hour period.
Swallow the tablet whole with a glass of water. You can take it with or without food, but note that a high-fat meal may delay absorption.
Avoid grapefruit juice while taking Viagra, as it can interfere with the medication’s metabolism and increase the risk of side effects.
The effects of Viagra usually last for four to five hours. Individual responses may vary.
If you experience any adverse effects, stop taking the medication and consult your doctor immediately.
Always discuss any potential drug interactions with your doctor before taking Viagra, especially if you are taking other medications for heart conditions, high blood pressure, or other health issues.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Always discuss Viagra use with your doctor before starting treatment. This ensures the medication is suitable for your health profile.
Common side effects include headaches, flushing, nasal congestion, and visual disturbances. These are usually mild and temporary. However, some individuals experience more serious effects.
- Heart problems: Viagra can lower blood pressure. If you have heart disease, talk to your doctor before using it. Chest pain, irregular heartbeat, or dizziness should prompt immediate medical attention.
- Vision changes: Sudden vision loss or changes in color vision require immediate medical consultation. This is a rare but serious side effect.
- Hearing problems: Sudden hearing loss or ringing in the ears (tinnitus) is another rare but serious side effect requiring immediate medical attention.
- Priapism: This is a prolonged, painful erection lasting more than four hours. It’s a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment. Contact emergency services immediately.
Several factors influence your risk of side effects. These include:
- Dosage: Higher doses increase the chance of side effects.
- Underlying health conditions: Pre-existing heart, liver, or kidney problems can increase the risk.
- Medications: Interactions with other medications are possible. Provide your doctor a complete list of your current medications and supplements.
- Age: Older individuals may have an increased sensitivity to side effects.
To minimize risks:
- Follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage precisely.
- Avoid grapefruit juice, as it can interfere with Viagra’s metabolism.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Report any unusual symptoms to your doctor promptly.
This information is for educational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs, herbal remedies, and recreational drugs. Certain combinations can be dangerous.
Nitrates and Viagra
Never combine Viagra with nitrates (found in medications for chest pain like nitroglycerin). This combination can cause a dangerously low blood pressure.
Alpha-Blockers
Alpha-blockers, used to treat high blood pressure and enlarged prostate, can interact with Viagra, potentially leading to dizziness and fainting. Your doctor might adjust your dosage.
Blood Thinners
Viagra may increase the risk of bleeding when taken with blood thinners like warfarin. Close monitoring by your doctor is necessary.
CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Medications that inhibit the CYP3A4 enzyme (like ketoconazole and erythromycin) can raise Viagra’s levels in your blood, increasing side effects. Your doctor may prescribe a lower dose.
Alcohol
Combining Viagra with alcohol can intensify side effects, particularly dizziness and low blood pressure. Moderate alcohol consumption is recommended, if any.
Grapefruit Juice
Avoid grapefruit juice while taking Viagra. It contains compounds that inhibit CYP3A4, potentially leading to elevated Viagra levels in the bloodstream.
Recreational Drugs
Combining Viagra with recreational drugs, especially those affecting the heart, can be extremely risky and should be avoided.
Other Medications
This list isn’t exhaustive. Discuss all your medications with your doctor before starting Viagra treatment to prevent potentially harmful interactions.